Introduction to Recyclable Nonwoven Fabric
Recyclable nonwoven fabric is a versatile material that has garnered significant attention in the realm of sustainable production. Unlike traditional woven textiles, nonwoven fabrics are created through a process that entangles fibers mechanically, thermally, or chemically, resulting in a fabric that is durable yet lightweight. The composition of these fabrics typically includes synthetic fibers, such as polypropylene or polyester, although natural fibers like cotton or hemp can also be used. This variety allows for an extensive range of applications, from medical supplies to personal protective equipment, and even household items.

The significance of recyclable nonwoven fabric lies in its potential to contribute to a more sustainable future. With increasing concerns about the environmental impact of textile waste, the development of recyclable options seeks to address these critical issues. Conventional fabrics often end up in landfills, where they can take hundreds of years to decompose. In contrast, recyclable nonwoven fabrics are designed with end-of-life considerations in mind, allowing for easier processing and regeneration into new products.
In today’s production landscape, where sustainability is a primary focus, the importance of recyclable nonwoven fabric cannot be understated. Companies are increasingly recognizing the need to adopt eco-friendly materials that align with their corporate social responsibility and set positive examples within their industries. Implementing recyclable nonwoven fabrics not only reduces waste but can also lower production costs in the long term. As both manufacturers and consumers become more conscious of their ecological footprints, recyclable nonwoven fabric offers a promising solution that meets the demands of modern-day sustainability practices.
The Importance of Recycling Nonwoven Fabrics
The recycling of nonwoven fabrics is a crucial component in the shift towards more sustainable manufacturing practices. Nonwoven fabrics are widely used across multiple industries, including medical, automotive, and consumer goods. However, the environmental impact of discarded nonwoven materials can be significant if they are not properly recycled. By recycling these fabrics, we can drastically reduce landfill waste, which is a growing concern as more products are disposed of each year.
One of the primary advantages of recycling nonwoven fabrics is resource conservation. Taking initiatives to recycle helps to recover raw materials that can be reused in the production process. This not only decreases the demand for virgin materials but also reduces the energy consumption associated with the extraction and processing of these resources. For instance, a study by the Environmental Protection Agency indicates that recycling one ton of textile waste can save approximately 3,000 gallons of water and reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly.
Additionally, the recycling of nonwoven materials plays a pivotal role in the reduction of pollution. Landfills produce harmful gases and leachate that can contaminate soil and groundwater. By diverting nonwoven fabrics from landfills and processing them through recycling facilities, we can mitigate these pollution risks. Reports show that recycling programs can lead to a 50% reduction in waste-related emissions, highlighting the impact of such initiatives in the textile sector.
The importance of recycling nonwoven fabrics extends beyond environmental benefits; it also has economic implications. The increased demand for recycled materials can spur job creation in the recycling and manufacturing sectors. In conclusion, the recycling of nonwoven fabrics represents a vital strategy for addressing both environmental concerns and economic opportunities within the larger fabric and textile industry.
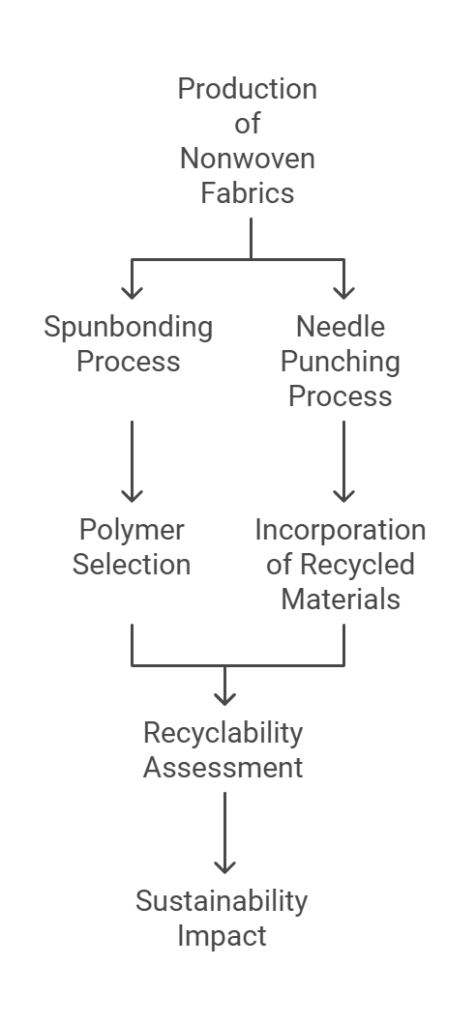
Manufacturing Processes of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics are produced through a variety of innovative methods that differ significantly from traditional textile manufacturing. Unlike woven or knitted fabrics, nonwoven materials are constructed by bonding fibers together using mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes. Two prominent techniques in the production of nonwoven fabrics are spunbonding and needle punching, each contributing to the unique properties and recyclability of the final product.
Spunbonding involves the extrusion of polymer fibers, which are laid down in a random arrangement and subsequently bonded together through thermal processes. This technique produces a lightweight, durable material that is commonly used in applications ranging from medical textiles to agricultural covers. The recyclability of spunbonded nonwovens largely depends on the type of polymer used; polypropylene, for instance, can be recycled effectively, while other blends may pose challenges. Understanding the polymer composition is crucial, as it directly impacts the sustainability of the product.
Needle punching, on the other hand, is a mechanical process where barbed needles are used to interlock fibers together. This method creates a thicker, more textured fabric, which is often chosen for heavier-duty applications such as insulation or geotextiles. The needle punching process allows for the use of various fiber types, including post-consumer recycled materials, thus enhancing the recyclability of the final product. The ability to incorporate recycled content is increasingly important as industries seek sustainable alternatives that reduce landfill waste.
Overall, the manufacturing processes of nonwoven fabrics play a significant role in determining their end-of-life options. As the demand for recyclable materials rises, advancements in production techniques and the selection of eco-friendly polymers are becoming critical in promoting sustainability within the nonwoven fabric industry.
Types of Recyclable Nonwoven Fabrics
Recyclable nonwoven fabrics can be categorized based on their composition, functionality, and end-use applications. The two primary types of fibers used in nonwoven fabric production are polyester and polypropylene, each possessing unique properties that contribute to their diverse applications in various industries.
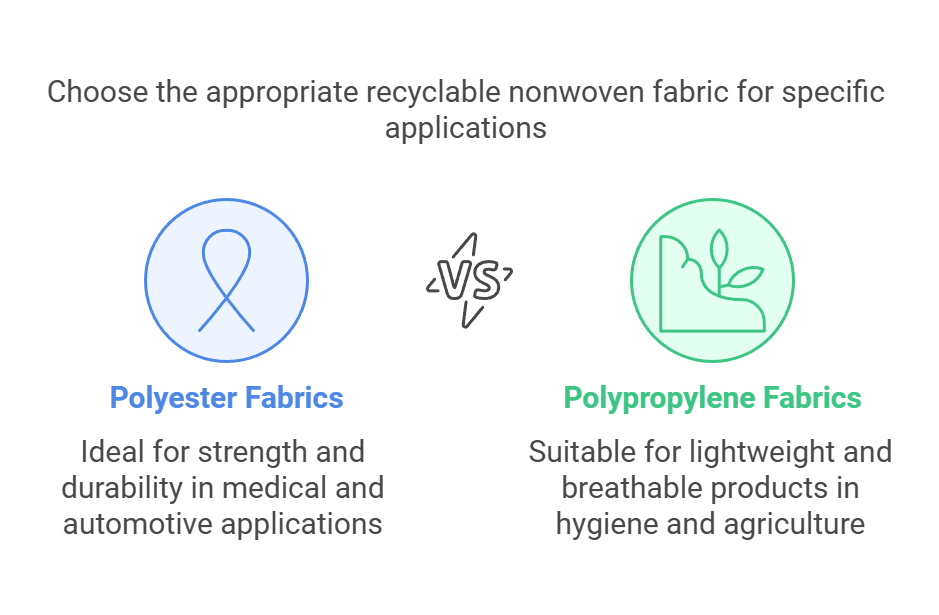
Polyester nonwoven fabrics are renowned for their strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching. This makes them particularly valuable in medical applications, such as surgical gowns and drapes, where both reliability and hygiene are paramount. Moreover, polyester nonwovens are increasingly used in the automotive industry, serving as insulation materials, components in interior linings, and even as filters. The recyclability of polyester nonwovens not only reduces waste but also allows for the repurposing of materials used in these critical sectors.
On the other hand, polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are lighter, more breathable, and less expensive to produce. This type of nonwoven fabric is commonly utilized in hygiene products like diapers and feminine products, where their absorbency plays a crucial role. Additionally, polypropylene nonwoven fabrics find applications in the production of geotextiles and agricultural covers due to their water-resistant qualities. Their ability to be recycled enhances their environmental appeal, allowing for a sustainable lifecycle in industries that generate substantial amounts of disposable products.
Moreover, both types of recyclable nonwoven fabrics can be utilized in personal protective equipment (PPE) and filtration systems, making them essential not only in medical settings but also in various industrial applications. By understanding and recognizing the different types of recyclable nonwoven fabrics, stakeholders across multiple sectors can make informed decisions that promote sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Innovative Recycling Methods
As the demand for sustainable practices intensifies, the recycling of nonwoven fabrics has gained significant traction in recent years. Innovative recycling methods, including chemical recycling, mechanical recycling, and upcycling approaches, have been developed to enhance the processing of these materials while minimizing environmental impact. These advancements reflect the industry’s commitment to finding eco-friendly solutions and promoting a circular economy.

Chemical recycling is one of the most promising methods for processing nonwoven fabrics. This technique involves breaking down the polymers used in the fabric into their basic building blocks, allowing for the creation of new materials that retain their original quality. By harnessing advanced technologies, such as depolymerization and solvent-based techniques, manufacturers can convert waste nonwoven materials back into usable resources. This process helps to reduce landfill waste while providing manufacturers with a sustainable supply of raw materials for creating recyclable nonwoven fabrics.
On the other hand, mechanical recycling focuses on physically processing the nonwoven fabrics without altering their chemical structure. In this approach, the used nonwoven materials are shredded, sorted, and reconstituted into new products. This method has gained popularity due to its efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to chemical recycling. Moreover, innovations in sorting technologies have improved the quality of recycled fibers, making them suitable for various applications. This fosters the creation of high-quality products while supporting the environment.
Additionally, upcycling is an emerging trend that seeks to creatively repurpose nonwoven fabrics into new items, offering both aesthetic and functional benefits. This practice often involves transforming discarded nonwoven materials into unique products, such as bags or home decor items. By giving new life to these fabrics, upcycling reduces waste and encourages consumers to embrace sustainable choices.
Overall, these innovative recycling methods not only address the challenges associated with nonwoven fabric disposal but also contribute significantly to sustainability within the industry. As technology advances, these approaches will continue to evolve, promoting a more responsible and sustainable future for nonwoven fabrics.
Challenges in Recycling Nonwoven Fabrics
The recycling of nonwoven fabrics presents multiple challenges that hinder their integration into sustainable waste management systems. One of the prominent issues is contamination. Nonwoven fabrics are often composed of various materials, including synthetic fibers like polypropylene or polyester, which complicates the recycling process. When these fabrics are mixed with other materials such as food waste or other textiles, it creates a scenario where the purity of the fibers is compromised. Contaminated materials often lead to lower quality recycled products and can even cause entire batches of recycling to be discarded, contributing to landfill waste.
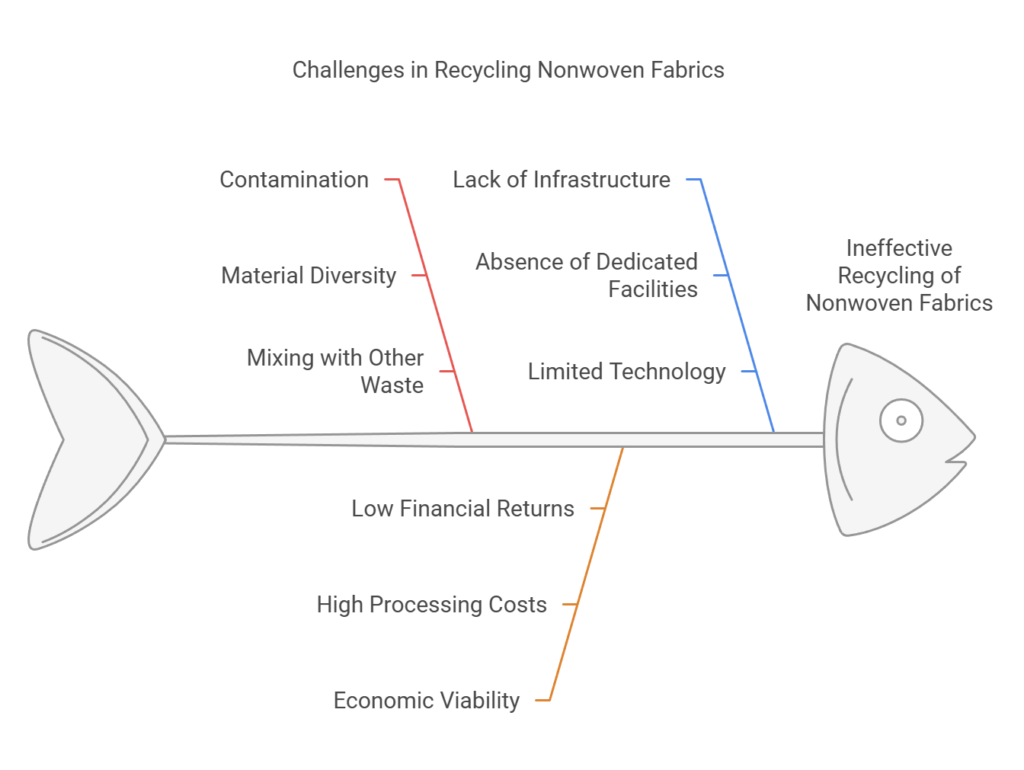
Another significant challenge lies in the economic viability of recycling nonwoven fabrics. The current recycling processes for these materials are not always cost-effective. The logistics of collecting, sorting, and processing nonwoven fabrics require substantial investment, yet the financial returns from recycled products may not justify these expenditures. As a result, many recycling facilities may hesitate to incorporate nonwoven fabrics into their operations. This situation calls for innovative economic models that could enhance the profitability of recycling nonwoven materials while decreasing the environmental impact.
Additionally, the lack of established recycling infrastructure complicates matters further. Unlike traditional textiles, which have a more developed network for recycling and processing, nonwoven fabrics do not benefit from a similar structure. This absence of dedicated facilities and technology limits the opportunities for effective recycling, making it difficult for manufacturers and consumers alike to contribute towards sustainability efforts. Addressing these challenges is crucial, as they impede the potential of nonwoven fabrics to be repurposed and reintegrated into the supply chain, thus affecting broader environmental goals.
Industry Applications of Recycled Nonwoven Fabrics
Recycled nonwoven fabrics have emerged as a versatile and environmentally friendly material, gaining traction across various industries. These fabrics, created from post-consumer waste and industrial by-products, can be repurposed into a wide array of applications that emphasize sustainability while maintaining functionality. One significant area of application is the production of reusable shopping bags. Retailers are increasingly adopting recycled nonwoven materials as an alternative to single-use plastic bags, thereby contributing to a reduction in plastic waste and promoting eco-conscious consumer habits.
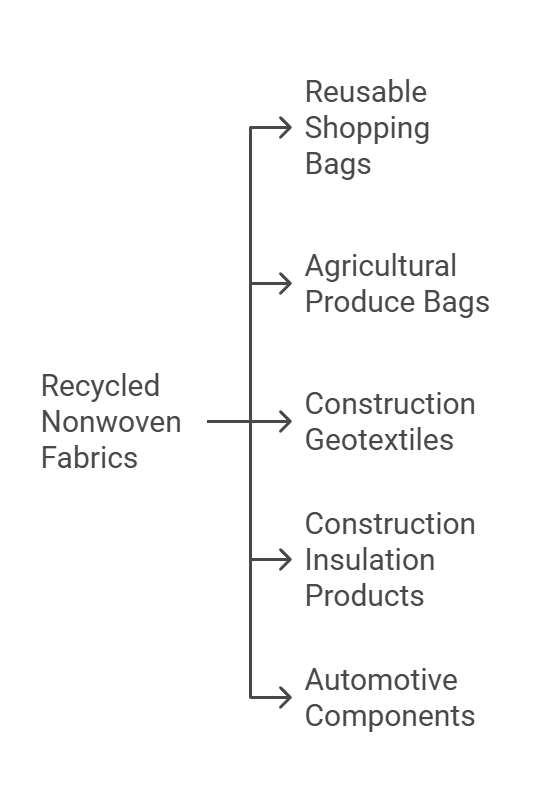
Another notable application can be found in the agricultural sector, particularly through the development of produce bags. Recycled nonwoven fabrics offer a breathable, lightweight solution for transporting fruits and vegetables, ensuring freshness and minimizing spoilage. Additionally, the durability and ease of manufacture of these fabrics mean they can replace traditional materials, reinforcing sustainability initiatives within food supply chains.
In the construction industry, recycled nonwoven fabrics are being utilized as geotextiles, which play a crucial role in soil stabilization and erosion control. These materials effectively separate soil layers while allowing for drainage, thus enhancing the longevity of structures. Moreover, recycled nonwoven fabrics have begun to feature in insulation products, helping to improve energy efficiency in buildings by using recycled materials to create high-performance barriers against heat transfer.
Furthermore, the automotive industry has also started to incorporate recycled nonwoven fabrics in various components, such as interior linings and sound insulation materials. This not only contributes to the reduction of waste but also streamlines the manufacturing process by utilizing material that is often lighter and more efficient than traditional options.
The application of recycled nonwoven fabrics demonstrates their versatility and essential role in promoting sustainability across multiple sectors. Investing in and expanding these applications is vital for advancing environmental efforts and reducing our reliance on virgin materials.
The Role of Consumers in Promoting Recycling
Consumers play a vital role in the recycling ecosystem, particularly when it comes to materials like nonwoven fabric. As the demand for recyclability increases, consumers can make informed decisions that directly influence the sustainability of products they purchase. One effective way to contribute to the recycling of nonwoven fabrics is by actively choosing recycled products. By selecting items made from or incorporating recycled nonwoven materials, consumers signal to manufacturers that there is a demand for such goods, encouraging further investment in sustainable practices.
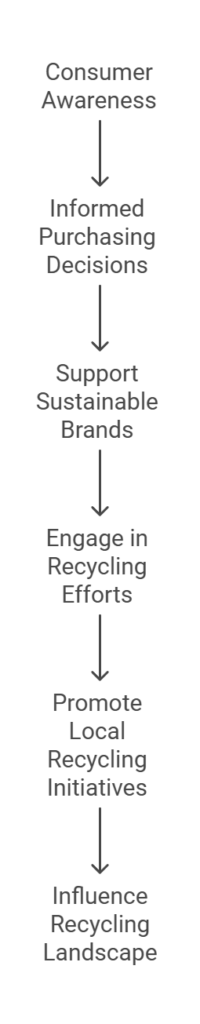
Supporting brands that prioritize sustainability is another essential aspect of consumer responsibility. Many companies are now integrating eco-friendly processes into their production methods, and by choosing to purchase from these brands, consumers help promote a business model that values environmental consciousness. Researching companies’ sustainability commitments—such as their use of recyclable nonwoven fabrics and their overall environmental impact—can empower consumers to make choices that align with their values.
Engaging in recycling efforts themselves represents a practical step consumers can take. This may involve participating in local recycling programs or seeking specialized recycling facilities that accept nonwoven materials. It is critical for consumers to familiarize themselves with the specific guidelines of their area, as recycling capabilities often vary. Additionally, individuals can educate others about the importance of recycling nonwoven fabrics and encourage communal efforts to enhance local recycling initiatives.
In essence, consumers hold significant influence over the recycling landscape. By becoming more aware of their purchasing choices, supporting sustainable brands, and engaging in proactive recycling practices, they can effectively promote a more sustainable use of nonwoven fabrics. As the journey toward a more environmentally-conscious society evolves, consumer involvement remains a key component in achieving meaningful change.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Recyclable nonwoven fabrics have garnered attention due to their potential environmental benefits. One key question often posed is, “What makes a nonwoven fabric recyclable?” Nonwoven fabrics are typically composed of synthetic or natural fibers that are bonded together, rather than woven. The recyclability of nonwoven fabrics largely depends on the type of material used. For instance, nonwovens made from polypropylene, polyester, or other thermoplastics can often be recycled in commercial recycling facilities. These materials can be melted down and repurposed into new products, thus diverting waste from landfills and contributing to a circular economy.
Another commonly asked question is, “How do I properly dispose of nonwoven fabrics?” Proper disposal is crucial to maximizing the environmental benefits of recyclable materials. It is recommended that consumers check with local recycling programs to determine whether nonwoven fabrics are accepted. Should they not be recyclable locally, these items can often still be repurposed in creative ways or donated, depending on their condition. Avoiding single-use nonwoven items, or choosing those that are clearly labeled for recycling, can also make an impact.
The question of “What is the future of nonwoven fabrics in sustainability?” is increasingly relevant. As awareness of environmental issues grows, the market for sustainable materials, including recyclable nonwoven fabrics, is expected to expand. Innovations are being made in fiber technology and recycling processes that enhance the viability of nonwoven fabrics as a sustainable option. Furthermore, consumer education about the recyclability of these materials will be essential to ensure responsible usage and disposal practices. With ongoing advancements, recyclable nonwoven fabrics hold promise for a more sustainable future.

8 Responses
Mating Press This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
Welcome! Glad you like it.
Noodlemagazine This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Thank you so much for your kind words and support! I’m glad you find my blog interesting and appreciate you sharing it. Looking forward to sharing more with you.
Noodlemagazine I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
Thank you for your kind words! We’re glad you enjoyed the article.
you are in reality a good webmaster The website loading velocity is amazing It sort of feels that youre doing any distinctive trick Also The contents are masterwork you have done a fantastic job in this topic
Thank you so much for your kind words! We strive to keep the site fast and the content top – notch. Glad you’re enjoying it.