Introduction to Nonwoven Fabric Technology
Nonwoven fabric technology represents a versatile and innovative approach to fabric production, distinct from traditional weaving and knitting processes. Nonwoven fabrics are created by bonding together fibers through various methods such as mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes, resulting in a sheet-like material that can possess unique properties. This technology has gained significant traction across a multitude of industries, including healthcare, automotive, and construction, owing to its adaptability and cost-effectiveness.
The importance of nonwoven fabrics lies in their functionality and wide array of applications. For instance, in the healthcare sector, they are crucial components in surgical masks, gowns, and other protective gear, providing essential barrier properties against pathogens. In the automotive industry, nonwoven fabrics are utilized for insulation, sound dampening, and filtration, improving vehicle performance and comfort. Furthermore, in construction, these materials serve as barriers and protectors against moisture and dirt, leading to enhanced longevity of structures.
Understanding nonwoven fabric technology is essential for professionals involved in material selection and application development. The advancements in nonwoven technology have led to innovations such as biodegradable options and specialized fabrics that cater to specific performance requirements, highlighting the growing significance of sustainable practices in manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve, the exploration of nonwoven fabrics will remain pivotal in providing solutions that address both functional needs and environmental concerns.
This comprehensive overview of nonwoven fabric technology sets the stage for a deeper examination of its manufacturing processes, properties, and emerging trends in subsequent sections. As the demand for nonwoven materials grows, awareness of their benefits and applications will be crucial for stakeholders aiming to leverage this technology effectively.
The Manufacturing Process of Nonwoven Fabrics
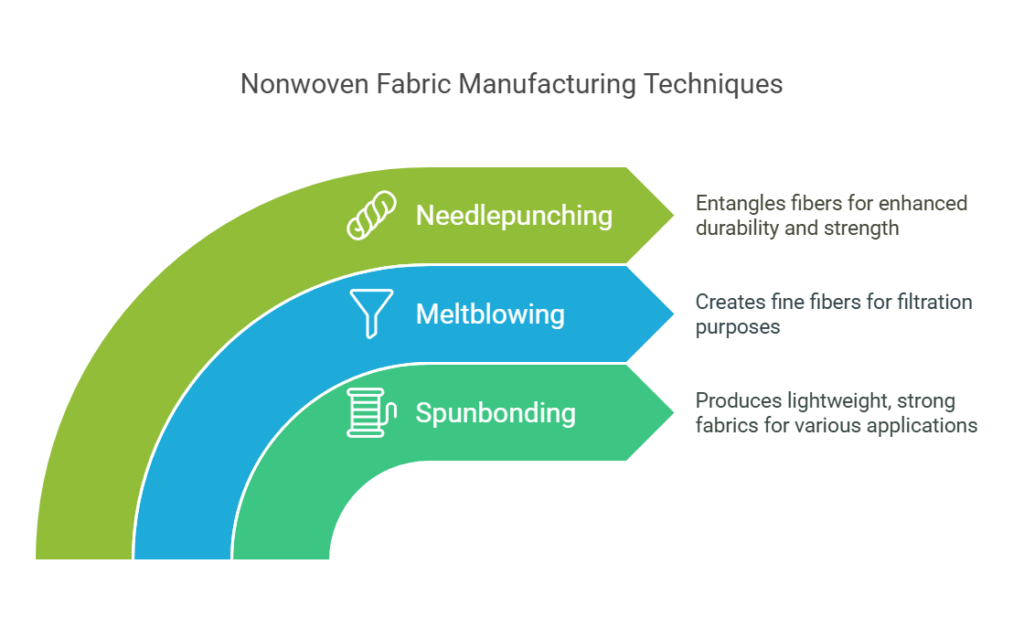
The production of nonwoven fabrics involves several distinct methods, each tailored to achieve unique characteristics and functional properties. The primary techniques include spunbonding, meltblowing, and needlepunching. Each method utilizes different machinery and processes to create fabric suitable for a wide array of applications.
Spunbonding is one of the most prevalent processes in nonwoven fabric manufacturing. In this method, thermoplastic polymers are melted and extruded through spinnerets to form continuous filaments. These filaments are then laid onto a conveyor belt, where they are bonded together using heat, pressure, or adhesives. This process is valued for its ability to produce lightweight yet strong fabrics, making it ideal for applications such as hygiene products, medical textiles, and geotextiles.
Meltblowing, on the other hand, focuses on producing fine fibers through a similar extrusion process. After the polymer is melted, high-velocity hot air is used to blow the molten polymer, resulting in ultrafine fibers. These fibers are collected on a substrate to form a web that can be thermally or mechanically bonded. Meltblown fabrics are particularly noted for their filtration properties, frequently used in the production of face masks and air filters due to their high surface area and porosity.
Needlepunching is a mechanical bonding process where multiple barbed needles are repeatedly punched through a web of fibers. As the needles penetrate the fiber mass, they entangle and interlock the fibers, resulting in a denser structure. This method allows the inclusion of various fiber types, offering diverse texture and durability. Needlepunching is extensively used in applications where enhanced strength and durability are required, such as carpets and industrial wipes.
Understanding these processes highlights the versatility of nonwoven fabric technology and its ability to cater to diverse industry requirements. Each manufacturing method contributes specific benefits, ensuring that nonwoven fabrics remain a vital component in modern textiles.
Types of Nonwoven Fabrics and Their Applications
Nonwoven fabrics represent a diverse category of materials that differ significantly from traditional woven fabrics. Their production process involves the bonding of fibers through various methods such as mechanical, thermal, or chemical means, resulting in a broad range of functional applications. Among the most common types of nonwoven fabrics are those made from polyester and polypropylene, alongside emerging biodegradable options that cater to the growing demand for sustainable materials.
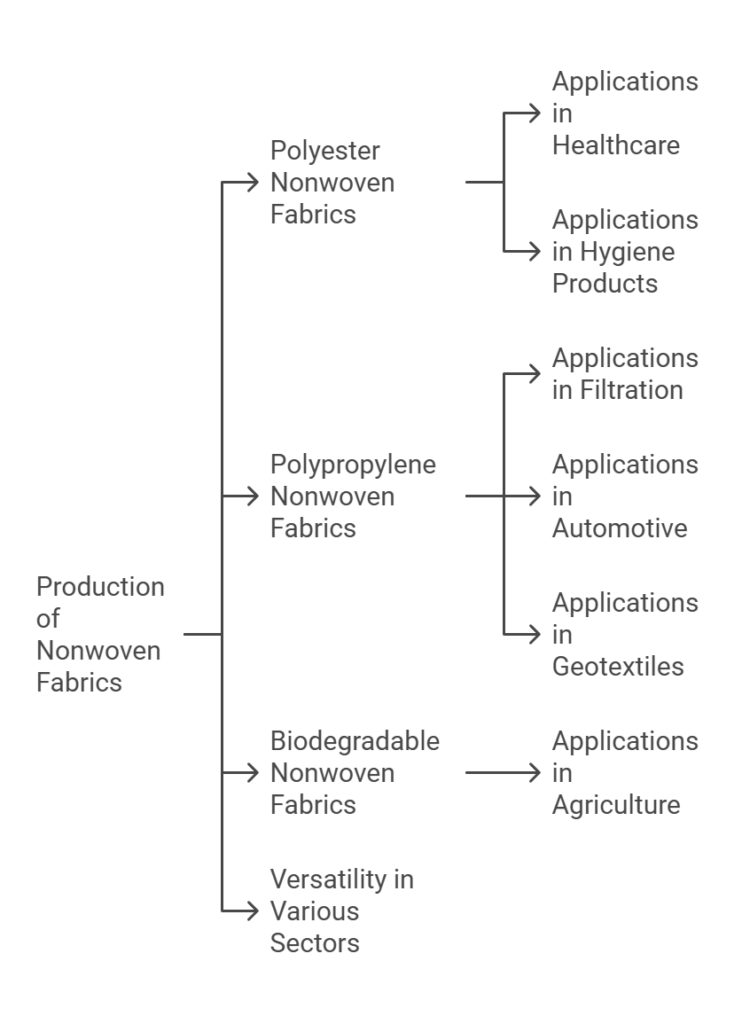
Polyester nonwoven fabrics are widely recognized for their durability and versatility. These fabrics exhibit excellent strength, resilience, and resistance to shrinking or stretching. Consequently, their applications are varied, spanning the healthcare sector, where they are used in surgical gowns, drapes, and face masks. Their moisture-wicking properties also make them suitable for use in hygiene products like diapers and feminine hygiene items.
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are another significant category, characterized by cost-effectiveness and lightweight nature. Their hydrophobic properties allow them to repel water, making them ideal for applications related to filtration. These fabrics are commonly employed in medical supplies, automotive interiors, and geotextiles for soil stabilization and erosion control in construction projects.
Moreover, the introduction of biodegradable nonwoven fabrics marks an important advancement in the industry, responding to environmental concerns. These fabrics, primarily derived from natural fibers or biodegradable polymers, are increasingly being adopted in agricultural applications such as mulch films and crop covers. Their ability to decompose after use aids in reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
The versatility of nonwoven fabrics extends into numerous sectors, including automotive for noise reduction, construction for insulation and vapor barriers, and even in consumer goods like reusable shopping bags. As technology advances, the development of new materials and applications for nonwoven fabrics continues to evolve, reflecting their significant role in various industries.
Advantages of Nonwoven Fabrics Over Woven and Knitted Fabrics
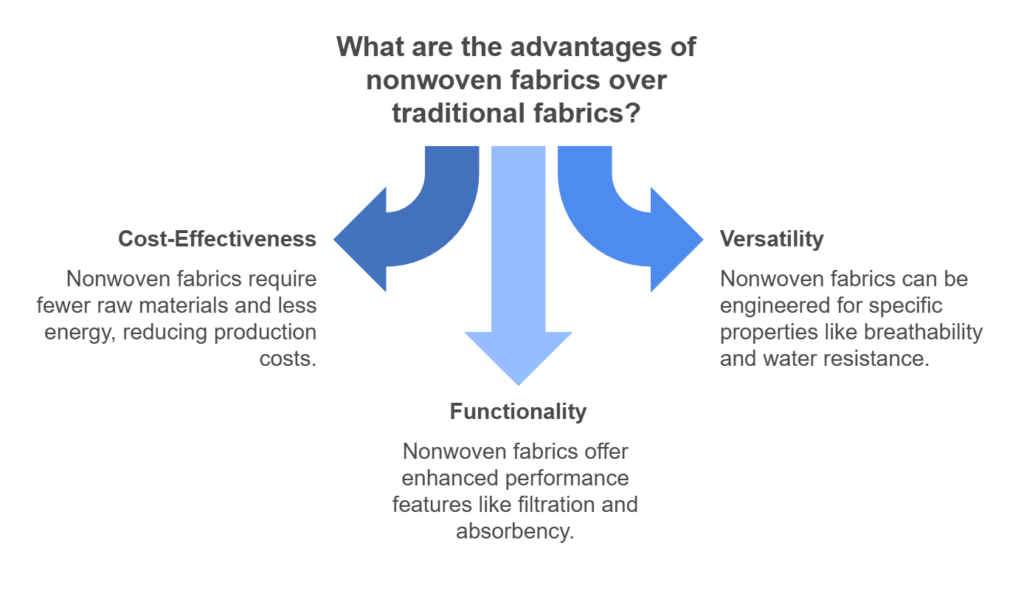
Nonwoven fabrics present a distinct set of advantages when compared to traditional woven and knitted fabrics, making them a preferred choice in various applications. One of the most significant advantages is cost-effectiveness. The manufacturing process of nonwoven fabrics typically requires fewer raw materials and less energy, which can significantly reduce production costs. This efficiency is particularly appealing in industries where budget constraints are common, allowing manufacturers to create high-quality products at lower prices.
Another key benefit of nonwoven fabrics is their versatility and customization options. Nonwoven technology enables producers to engineer fabrics with specific properties tailored to meet diverse needs. For instance, nonwoven materials can be designed to be lightweight, breathable, and water-resistant, making them suitable for applications ranging from medical supplies, such as surgical gowns and masks, to household items like diapers and cleaning products. In contrast, woven and knitted fabrics have limitations in terms of customization, primarily due to their inherent structural constraints.
Functionality is a crucial area where nonwoven fabrics excel. The unique fabrication process allows for the incorporation of various fibers and additives, enhancing the material’s performance. For instance, nonwoven fabrics can possess excellent filtration capabilities, making them ideal for use in air and liquid filtration systems. Additionally, they can be engineered to provide improved absorbency and durability, which are essential traits in products designed for healthcare and hygiene purposes. Woven and knitted fabrics, while functional in their own right, often fall short in achieving the specialized performance characteristics that nonwoven fabrics can deliver.
Overall, the combination of cost-effectiveness, customization, and functional advantages contributes to the growing popularity of nonwoven fabrics across multiple sectors, establishing them as a valuable alternative to woven and knitted fabrics.
Environmental Impact of Nonwoven Fabrics
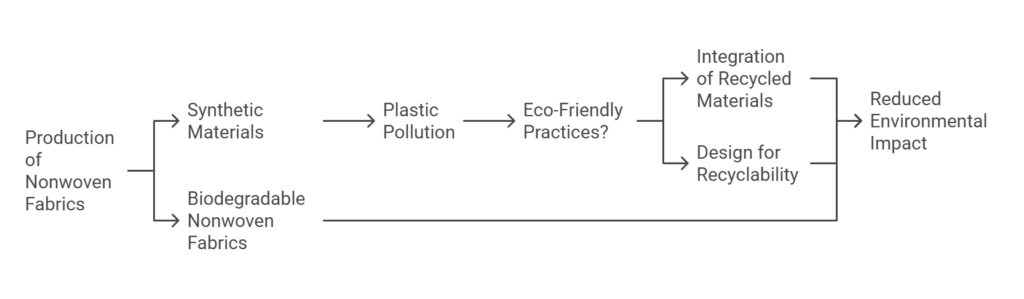
The production and utilization of nonwoven fabrics have become a focal point of discussion in recent years, particularly concerning their environmental implications. On one hand, nonwoven fabrics are often manufactured from synthetic materials, primarily polypropylene, which poses challenges related to plastic pollution. The durability and widespread use of these materials can contribute significantly to waste accumulation, especially when products are designed for single-use applications. The disintegration of nonwoven fabrics in landfills takes longer than natural fibers, thereby exacerbating concerns over long-term environmental sustainability.
Conversely, there are noteworthy advancements in the field of nonwoven fabric technology that aim to mitigate these negative impacts. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as integrating recycled materials into the production process. These materials not only help reduce reliance on virgin resources but also decrease the energy footprint associated with fabric manufacturing. Furthermore, many nonwoven products are designed to be more recyclable, helping to close the loop in the textile lifecycle.
In recent years, the advent of biodegradable nonwoven fabrics has emerged as a promising solution. These innovative materials are engineered to break down more readily in natural environments, thus reducing their long-term impact on ecosystems. Biodegradable nonwovens are typically made from natural fibers and bioplastics, enabling them to decompose under the right conditions. This transition towards more sustainable fabric options is driven by consumer demand for eco-conscious products and the industry’s need to address regulatory pressures regarding waste management.
Overall, while the environmental challenges posed by traditional nonwoven fabrics cannot be overlooked, the commitment to sustainable practices and materials within the industry signals a positive shift towards reducing the ecological footprint of these versatile textiles.
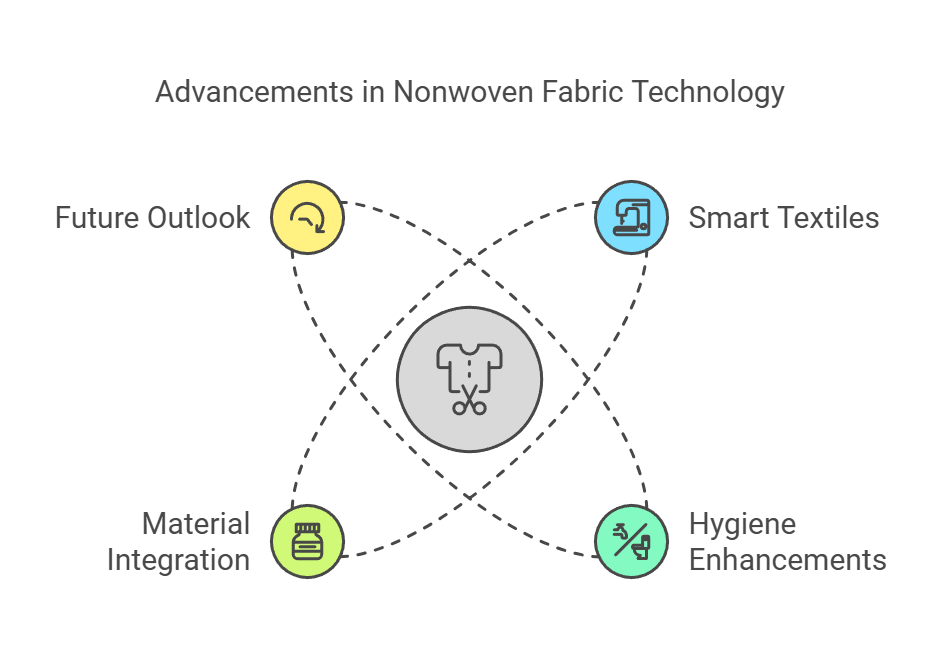
Innovations in Nonwoven Fabric Technology
The nonwoven fabric industry has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, driven by technological innovations and evolving consumer demands. One of the most notable trends is the development of smart textiles. These fabrics integrate electronics and sensors, enabling functionalities such as moisture control, temperature regulation, and even health monitoring. Smart nonwoven textiles are finding applications in various fields, including healthcare, sportswear, and automotive, showcasing their versatility and potential to improve user experiences.
Another critical advancement in nonwoven fabric technology is the enhancement of hygiene properties. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on creating fabrics that exhibit antimicrobial and antiviral characteristics. Such innovations are particularly important in sectors like healthcare and personal care, where the need for high-level cleanliness and safety is paramount. The incorporation of specialized treatments and biodegradable fibers has made it possible to produce nonwoven materials that not only meet regulatory standards but also promote sustainability, addressing growing environmental concerns.
Integration with other materials marks another significant trend in the evolution of nonwoven fabrics. Hybrid materials, which combine nonwoven textiles with woven fabrics, foams, or films, are enhancing durability and performance. This integration allows for the development of materials with improved breathability, strength, and aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for various applications from protective clothing to home furnishings.
The future outlook for nonwoven fabric technology remains promising. Ongoing research and development efforts are expected to introduce additional innovations, such as sustainable and bio-based materials. As industries continue to seek solutions to pressing environmental and performance-related challenges, nonwoven fabric technology is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of textiles.
Challenges Faced by the Nonwoven Fabric Industry
The nonwoven fabric industry is confronting a myriad of challenges that impede its growth and innovation. One significant obstacle is the competition posed by traditional fabric manufacturers. These manufacturers, who typically produce woven and knitted fabrics, often benefit from established supply chains, customer loyalty, and economies of scale. As a result, nonwoven fabric producers must differentiate their products, emphasizing unique qualities such as cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatility to attract potential customers. The challenge is further intensified by the presence of low-cost alternatives, which leads to price wars that can impact profit margins across the entire nonwoven sector.
Another pressing issue revolves around the sourcing of sustainable materials. As environmental concerns rise, consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products. Nonwoven fabric manufacturers are thus under pressure to incorporate recycled and biodegradable materials into their processes. However, sourcing these materials can be problematic due to availability issues and higher costs linked to sustainable production methods. Furthermore, manufacturers must invest in research and development to ensure that these materials do not compromise the quality and performance that nonwoven fabrics are renowned for.
Moreover, compliance with regulatory standards presents a formidable challenge for the industry. Nonwoven fabrics are utilized in various applications, including healthcare, automotive, and construction. Each sector has specific compliance requirements, which can vary by region. Navigating these regulations necessitates substantial resources to ensure that products are safe and meet industry standards. This can be particularly daunting for smaller nonwoven fabric manufacturers, who may lack the expertise or financial backing to manage compliance effectively. Addressing these challenges is essential for the nonwoven fabric industry to sustain growth and compete effectively in a rapidly evolving market.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have garnered significant attention in various industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. One prime example lies in the healthcare sector, where nonwoven materials are utilized for the production of surgical gowns and masks. These disposable items have become essential in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Their inherent breathability, fluid resistance, and ability to filter bacteria make them superior to traditional woven fabrics, thereby enhancing the overall safety of medical personnel and patients alike.
In the automotive industry, nonwoven fabrics are employed extensively for insulation materials and interior linings. These fabrics help reduce noise and improve thermal management within vehicles. For instance, manufacturers often use nonwoven polypropylene for sound deadening panels due to its lightweight nature and excellent acoustic properties. This application not only enhances passenger comfort but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle by improving insulation.
The agricultural sector has also seen the successful use of nonwoven fabrics, particularly in the form of crop covers and geotextiles. Nonwoven fabric used as crop covers aids in temperature regulation and protection against pests, thus promoting healthier plant growth. In geotechnical applications, nonwoven geotextiles provide drainage and erosion control, showcasing their ability to improve soil stability and enhance water management systems.
Lastly, the filtration industry has benefited immensely from nonwoven technology. Nonwoven fabrics are widely used in air and liquid filtration systems due to their effective particle retention capabilities. For example, HVAC systems utilize nonwoven air filters, which enhance indoor air quality while promoting energy efficiency by reducing airflow resistance.
These case studies exemplify the remarkable versatility and effectiveness of nonwoven fabrics across various sectors, illustrating how they provide tailored solutions to specific challenges while enhancing product performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have gained significant attention in various industries due to their versatility and functionality. However, several common questions often arise regarding their properties, applications, and manufacturing processes.
What are nonwoven fabrics made from?
Nonwoven fabrics can be composed of natural fibers, synthetic materials, or a blend of both. Common fiber types include polypropylene, polyester, and viscose. The choice of material depends on the intended application, as each fiber type offers unique benefits in terms of durability, softness, and absorbency.
Are nonwoven fabrics environmentally friendly?
The environmental impact of nonwoven fabrics varies with the materials used. Biodegradable options made from natural fibers are available, providing a lower environmental footprint. However, many synthetic nonwovens are recyclable and can be reused in other applications. It is crucial for consumers to research specific products and their disposal options to make informed choices.
How can I incorporate nonwoven fabrics in my projects?
Numerous industries utilize nonwoven fabrics, from healthcare to automotive and apparel. Depending on the application, users can employ nonwoven materials for disposable masks, filters, insulation, and geotextiles. To effectively integrate nonwoven fabrics into your projects, consider factors such as weight, durability, and moisture resistance that align with your specific needs.
What is the future of nonwoven technology?
Innovation in nonwoven fabric technology continues to grow, with advancements focusing on enhancing material performance and sustainability. Research and development aim to create fabrics that are more breathable, durable, and environmentally friendly. As industries increasingly prioritize eco-conscious choices, nonwoven technology is expected to lead the way in sustainable textile solutions.
These frequently asked questions highlight just a few aspects of nonwoven fabrics. As demand for innovative materials increases, it is essential to stay informed about their properties and potential applications.

2 Responses
I was suggested this web site by my cousin Im not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble You are incredible Thanks
Thanks for your comment! Glad you find our website useful. 😊