Introduction to Nonwoven Fabric Production
Nonwoven fabrics represent a unique category of textile materials that are manufactured through a process of bonding fibers together, producing a fabric that does not undergo traditional weaving or knitting methods. Unlike their woven counterparts, which involve interlacing threads, nonwoven fabrics are created directly from fibers using mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes. This innovative technique allows for the creation of materials with diverse properties and functionalities tailored to a variety of applications.
The significance of nonwoven fabrics is profound, as they serve numerous sectors including healthcare, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. In the healthcare industry, for instance, nonwoven materials are extensively used in the production of medical gowns, masks, and surgical drapes, providing essential barriers against contamination while remaining lightweight and breathable. Similarly, in the automotive sector, nonwoven fabrics are utilized for insulation, interior linings, and filtration systems, contributing to enhanced comfort and performance.
Nonwoven fabrics are favored for their cost-effectiveness and efficiency in production. The manufacturing process often requires less water and energy compared to traditional fabric production methods, making it an environmentally conscious choice. Additionally, nonwoven materials exhibit advantageous characteristics such as enhanced absorbency, filtration efficiency, and durability, broadening their applicability across various industries.
The versatility of these fabrics allows them to be engineered for specific functions, leading to continued innovation in this domain. As industries seek more sustainable and functional material solutions, nonwoven fabric production is poised for growth, with advancements in technology continually enhancing product quality and capabilities. This introduction sets the foundation for a deeper exploration of the processes involved in producing nonwoven fabrics, their vast applications, and the benefits they offer over conventional woven textiles.
What Are Nonwoven Fabrics?
Nonwoven fabrics are innovative textile materials characterized by their unique manufacturing processes, which differentiate them significantly from traditional woven or knitted textiles. Unlike woven fabrics that are produced by interlacing threads, nonwoven fabrics are created by bonding or felting fibers together through mechanical, chemical, or thermal means. This process results in a fabric that does not have a distinct grain or directional pattern, offering numerous advantages in various applications.
The composition of nonwoven fabrics can vary widely, encompassing synthetic fibers such as polypropylene and polyester, as well as natural fibers like cotton and pulp. These materials can be processed to meet specific performance criteria, such as strength, absorbency, or barrier properties. As a result, nonwoven fabrics are incredibly versatile, making them suitable for diverse applications, including medical supplies, filtration systems, geotextiles, and consumer goods.
One of the defining characteristics of nonwoven fabrics is their ability to be produced in a continuous sheet, allowing for efficient mass production. The processes involved in creating nonwoven fabrics include methods such as spunbonding, meltblowing, and needle punching, each imparting different qualities to the final product. For instance, spunbonded nonwovens are often known for their durability and lightweight properties, making them ideal for use in products like clothing and hygiene items.
In addition to their varied compositions and manufacturing techniques, nonwoven fabrics are also recognized for their eco-friendliness. Many nonwoven materials are recyclable or biodegradable, appealing to the growing demand for sustainable products. In summary, nonwoven fabrics are an essential aspect of the textile industry, providing advantageous characteristics and responses to modern consumer needs through innovative production methods.
The Production Process of Nonwoven Fabrics
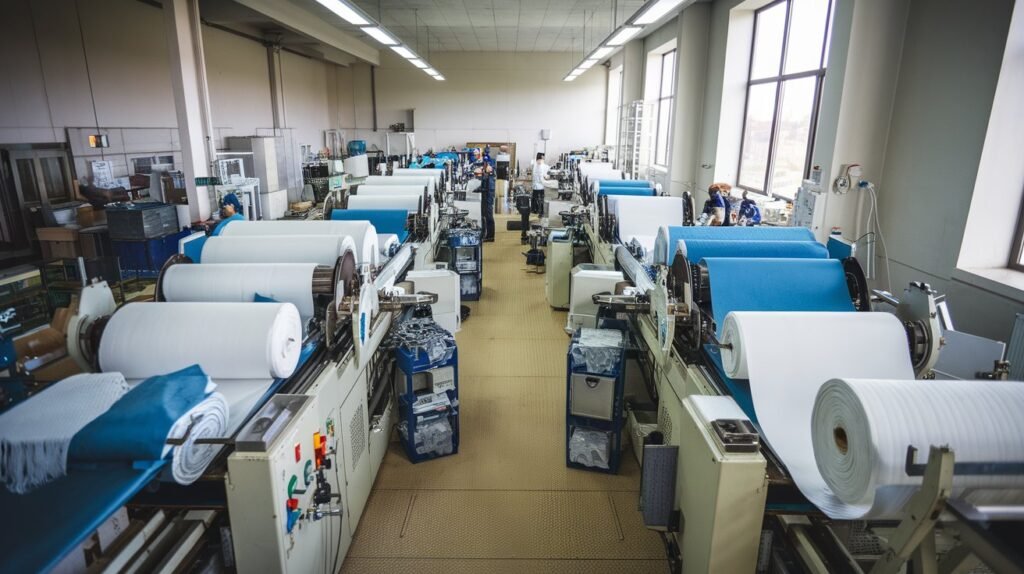
The production of nonwoven fabrics encompasses a variety of steps and methods, each contributing to the unique characteristics of the final product. Unlike traditional woven fabrics, which are made by interlacing yarn, nonwoven fabrics are created by bonding fibers together through various techniques, leading to fabrics that offer distinct advantages in terms of performance and functionality.

One of the primary methods used in producing nonwoven fabrics is spunbonding. This technique involves extruding filament fibers, which are then laid down in a web-like structure and subsequently bonded to create a strong, durable fabric. This process is highly efficient and produces lightweight fabrics that are ideal for applications such as medical garments, agricultural covers, and personal protective equipment.
Another well-known method is meltblowing, which is particularly favored for manufacturing high-performance fabrics with fine fibers. In this process, thermoplastic polymer is melted and extruded through a spinneret, forming extremely fine filaments that are blown by high-velocity hot air. These fibers rapidly cool and land on a conveyor belt, creating a web. The resulting nonwoven fabric is known for its excellent filtration properties, making it widely used in air and liquid filtration applications.
Needlepunching is yet another critical technique in the production of nonwoven fabrics. It involves mechanically entangling fibers using barbed needles, resulting in a dense and resilient material. This method is especially effective for creating textured surfaces and thicker nonwoven fabrics, which are prevalent in applications like automotive interiors, geotextiles, and insulation materials.
Each production method has its unique advantages, enabling manufacturers to select the most suitable technique based on the desired properties of the final product. The versatility of nonwoven fabric production allows it to meet diverse industrial and consumer needs, thereby solidifying its importance in modern material science.
Materials Used in Nonwoven Fabric Production
Nonwoven fabrics are engineered textiles that do not involve weaving or knitting processes. A variety of raw materials are employed in their production, with polypropylene, polyester, and rayon being the most common. Each of these materials contributes unique properties that enhance the performance and functionality of the final product.
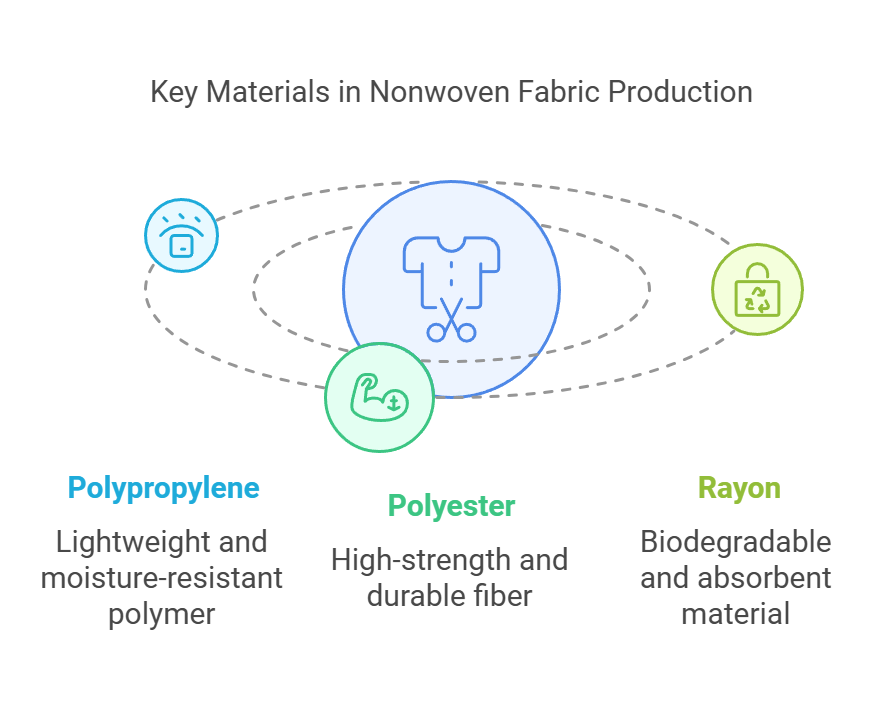
Polypropylene is arguably the most widely used material in nonwoven fabric production due to its favorable attributes. This thermoplastic polymer is lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant, making it an ideal choice for disposable products and applications where hygiene is crucial, such as medical gowns and diapers. Additionally, polypropylene can be easily processed and manipulated, allowing manufacturers to create nonwoven fabrics in diverse textures and weights.
Another significant material is polyester, known for its high strength and resistance to stretching and shrinking. Polyester nonwoven fabrics exhibit excellent resilience and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including home furnishings, automotive interiors, and filtration systems. This material also has a low absorbency level, giving polyester nonwoven fabrics their water-repellent and stain-resistant characteristics, which are essential for many end-use products.
Rayon, which is derived from natural sources such as wood pulp, is another commonly used material in nonwoven fabric production. This semi-synthetic fiber possesses a soft texture and excellent absorbency, making it an ideal choice for personal care items like sanitary napkins and wipes. Furthermore, rayon nonwoven fabrics are biodegradable, aligning them with environmentally sustainable practices and appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
In summary, the choice of materials in nonwoven fabric production significantly impacts the characteristics and applications of the fabrics. By utilizing polypropylene, polyester, and rayon, manufacturers can create versatile products that meet diverse consumer needs while maintaining performance and sustainability.
Applications of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have gained significant traction across various industries, primarily due to their versatility and unique properties. One notable sector is the medical field, where nonwoven materials are crucial for the production of surgical drapes, gowns, and masks. These fabrics offer excellent barrier protection against fluids and microbes, ensuring safety and hygiene in clinical settings. Their lightweight and breathable characteristics enhance comfort for both patients and healthcare personnel, making them indispensable in health care applications.

Similarly, the automotive industry utilizes nonwoven fabrics for a variety of applications. Nonwovens serve as insulation, sound absorption materials, and filter fabrics in vehicles. Their lightweight nature contributes to fuel efficiency by reducing the overall weight of the vehicle. Furthermore, nonwoven materials are employed in seat lining, headliners, and carpets, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and functionality. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in the automotive sector underscores the significance of nonwoven fabrics in contemporary vehicle design.
The construction industry also benefits from the application of nonwoven fabrics, where they are utilized in geotextiles, roofing materials, and insulation products. These fabrics serve crucial roles in enhancing moisture control, providing durability, and facilitating soil reinforcement. Nonwoven geotextiles can prevent erosion and improve drainage, thus contributing to the longevity of construction projects. Moreover, in insulation applications, their thermal properties help in energy conservation, making them a popular choice among builders and contractors.
Lastly, in the realm of consumer goods, nonwoven fabrics are commonly found in products such as disposable diapers, feminine hygiene products, and home textiles. These fabrics combine absorbency with comfort and durability, ensuring user satisfaction. The diversity of applications across multiple sectors illustrates the integral role of nonwoven fabrics in modern industrial practices.
Advantages of Nonwoven Fabrics over Woven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics offer a range of significant advantages compared to traditional woven fabrics, positioning them as a valuable option across diverse industries. One of the primary benefits of nonwoven fabrics is their cost-effectiveness. The production process of nonwoven materials is typically less labor-intensive and requires fewer raw materials, which leads to reduced manufacturing costs. As a result, these fabrics can be produced in bulk at a lower price, making them an economical choice for manufacturers and consumers alike.
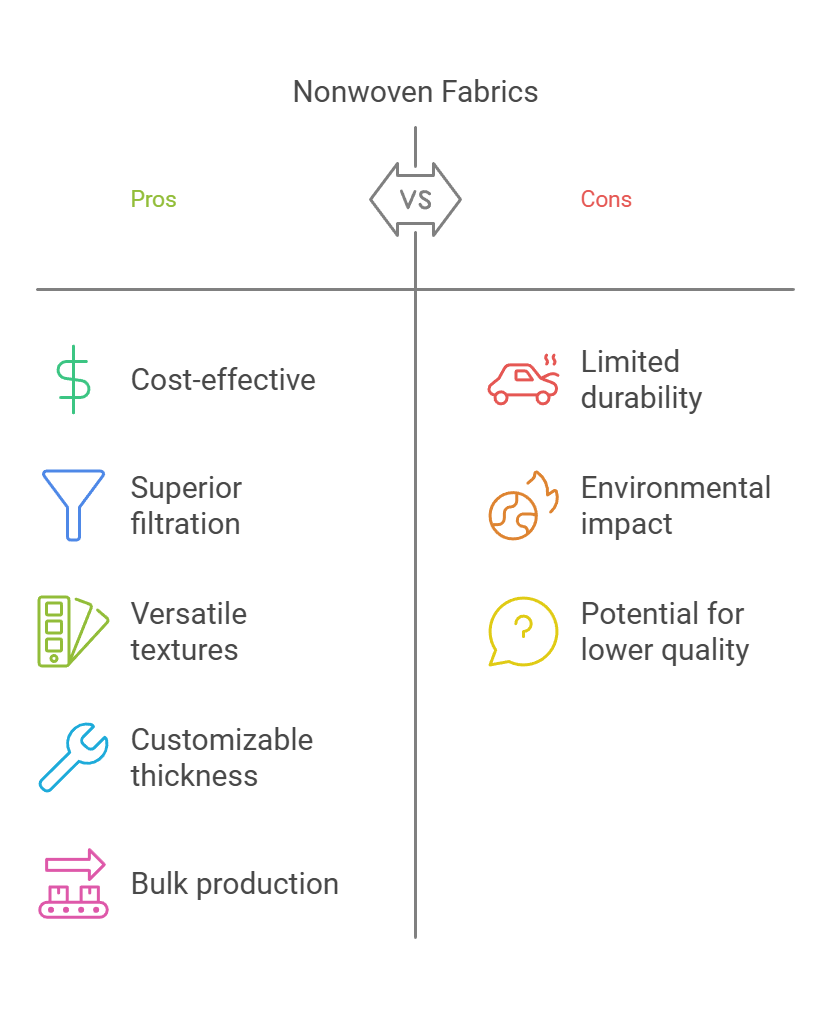
In addition to their affordability, nonwoven fabrics are recognized for their superior filtration properties. This characteristic makes them particularly ideal for use in applications such as medical masks, air and liquid filtration systems, and even insulation materials. Nonwoven filters can trap particles more efficiently due to their unique structure, which consists of randomly arranged fibers that create a complex network. This allows for enhanced performance in terms of capturing airborne pollutants and providing protective barriers.
Another notable advantage of nonwoven fabrics lies in their ability to provide varying thickness and texture options. This flexibility allows manufacturers to customize the fabric to achieve specific qualities suitable for numerous applications. For instance, nonwoven fabrics can be engineered to be soft and absorbent for hygienic products, or tougher and more durable for construction and automotive applications. This versatility makes nonwoven fabrics a preferred choice in sectors ranging from healthcare and hygiene to agriculture and packaging.
Overall, the combination of cost efficiency, exceptional filtration capabilities, and the adaptability to meet various application requirements underlines the advantages of nonwoven fabrics over their woven counterparts. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for nonwoven options is expected to grow, solidifying their role in modern fabric production.
Environmental Considerations in Nonwoven Fabric Production
Nonwoven fabric production, while essential in various applications, has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As the demand for these materials grows, it is crucial to adopt sustainable practices that mitigate adverse environmental effects. This involves utilizing eco-friendly raw materials, such as recycled plastics or biodegradable fibers, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing process.
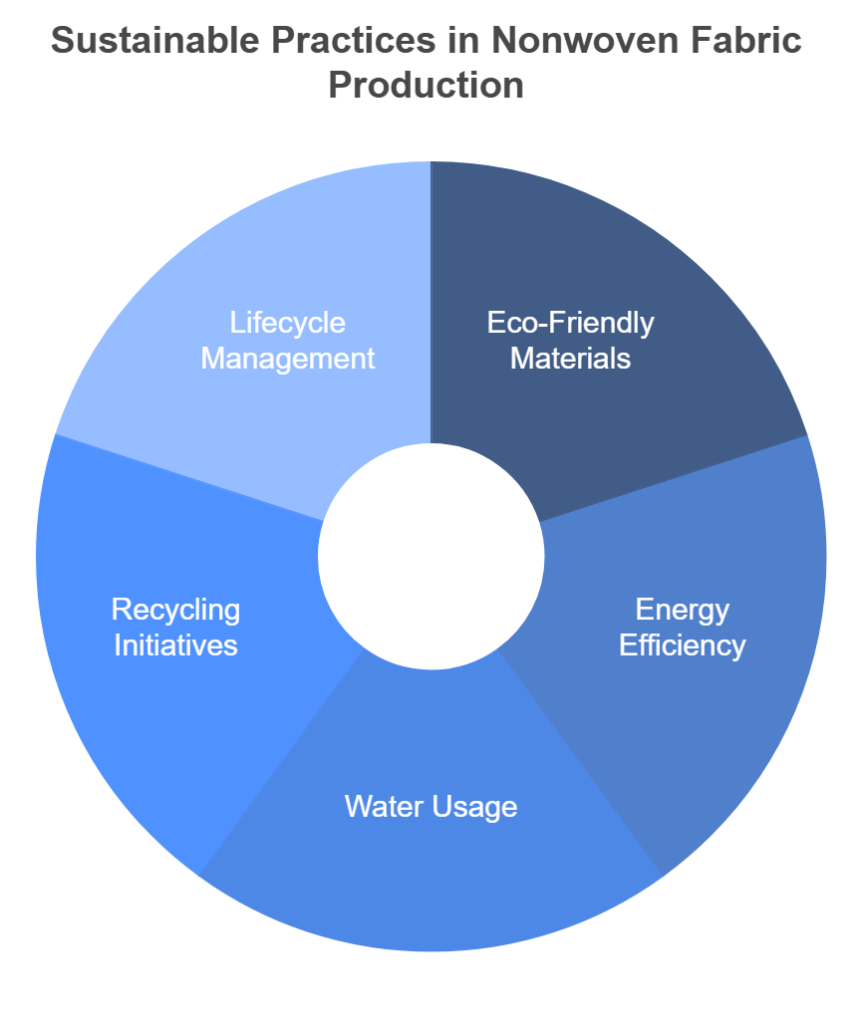
Additionally, the production of nonwoven fabrics involves considerable energy consumption and water usage. Therefore, manufacturers are increasingly looking at energy-efficient technologies and processes that minimize resource use. For instance, employing closed-loop water systems can limit water waste, while renewable energy sources can help decrease reliance on fossil fuels during production.
Recycling options for nonwoven fabrics are also an important aspect of sustainability. Although many nonwoven fabrics have historically been challenging to recycle due to their composition, advancements in technology have led to the development of recyclable nonwoven options. These innovations enable the recovery of materials at the end of a product’s lifecycle, allowing for reintegration into the production process. Furthermore, manufacturers are encouraged to provide take-back programs, facilitating responsible disposal and recycling practices for consumers.
The lifecycle of nonwoven products is another critical component of their environmental impact. Understanding how these materials are sourced, produced, used, and ultimately disposed of can help identify areas for improvement. Implementing a circular economy model, where products are designed for longevity and recyclability, can significantly enhance sustainability. This approach not only reduces waste but also promotes resource conservation and environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, the environmental footprint of nonwoven fabric production can be addressed through sustainable practices, energy-efficient processes, recycling initiatives, and a comprehensive understanding of product lifecycles, fostering a balance between utility and ecological responsibility.
Future Trends in Nonwoven Fabric Technology
The nonwoven fabric industry is poised for significant growth, driven by various emerging trends that reflect both technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. One prominent trend is the increasing focus on eco-friendly materials. As sustainability becomes a cornerstone of manufacturing practices, the shift towards bio-based raw materials, recycled fibers, and biodegradable components is gaining momentum. Manufacturers are exploring plant-based polymers and organic fibers as alternatives to petroleum-based inputs, aiming to reduce the environmental footprint of nonwoven products.

Advancements in production techniques are also on the horizon. Modern manufacturers are investing in innovative technologies such as meltblown and spunbond processes that enhance the efficiency and versatility of nonwoven fabric production. These innovations not only lead to cost-effective production but also improve the performance characteristics of nonwoven fabrics, catering to specific market needs. For instance, high-performance nonwovens, featuring enhanced filtration capabilities and optimized mechanical properties, are increasingly sought in the medical and hygiene sectors.
Additionally, the versatility of nonwoven fabrics is leading to potential new applications across various growing sectors. In the automotive industry, for example, nonwoven materials are being utilized for interior components, contributing to weight reduction and improved acoustics. Similarly, the construction sector is exploring the use of nonwovens for geotextiles in landscaping, erosion control, and reinforcement applications. The adaptability of nonwoven fabric technology allows it to address diverse needs, positioning it as a transformative material in numerous industries.
As the landscape of nonwoven fabric technology continues to evolve, stakeholders within the industry remain focused on harnessing these innovations to meet future challenges. Sustainable practices, advanced production methods, and an emphasis on versatile applications will define the trajectory of nonwoven fabric technology in the coming years, ensuring its relevance in a rapidly changing global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have gained significant attention in various industries due to their versatility and unique properties. Below, we address some common questions regarding nonwoven fabric production, durability, maintenance, and safety standards.
What are nonwoven fabrics made of? Nonwoven fabrics are typically created using synthetic fibers, such as polypropylene or polyester, as well as natural fibers like cotton or cellulose. The choice of materials varies depending on the intended application of the fabric. The fibers are bonded together through various processes including heat, chemical adhesives, or mechanical entanglement, resulting in a textile that does not undergo traditional weaving or knitting processes.
How durable are nonwoven fabrics? The durability of nonwoven fabrics can vary greatly based on the production methods and materials used. Generally, they are known for their strength and resistance to tearing, making them suitable for applications that require robust materials. For example, nonwoven fabrics are commonly used in hygiene products, medical textiles, and geotextiles, all of which benefit from their durability.
What maintenance is required for nonwoven fabrics? Maintenance for nonwoven fabrics typically involves regular cleaning. Most nonwoven textiles can be easily washed, but their cleaning procedure can depend on the specific fabric type and its intended use. For example, some nonwoven fabrics are designed to be disposable, while others may be reusable and require laundering. Always follow manufacturer’s guidelines for care to maintain the integrity of the fabric.
Are nonwoven fabrics safe to use? Yes, nonwoven fabrics are generally considered safe, especially when produced according to established safety standards. Manufacturers often adhere to guidelines relevant to their applications, ensuring that nonwoven fabrics used in healthcare or food packaging meet strict regulatory requirements. It’s pivotal to verify certifications for specific applications to ensure safety compliance.
How do nonwoven fabrics compare to traditional fabrics? Unlike traditional woven or knitted fabrics, nonwoven fabrics provide distinct advantages, including lower production costs, versatility in applications, and a wide range of properties tailored for specific uses. While traditional fabrics excel in certain applications due to their aesthetic appeal and drape, nonwoven fabrics are favored in industries that prioritize functionality and efficiency.
Understanding these FAQs about nonwoven fabrics is essential for making informed decisions regarding their use and production in various industries.

12 Responses
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Thank you for your kind words! Glad you like our content. Looking forward to your continued visits.
Henof naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Thank you for your feedback. We will pay attention to spelling issues and improve our website. Looking forward to your next visit.
Blue Techker I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
Thanks! Glad you like it. 😊
I just could not leave your web site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person supply to your visitors Is gonna be again steadily in order to check up on new posts
Thank you for your kind words! We’ll keep providing valuable content. Looking forward to your next visit.
Noodlemagazine This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Diverse Non Woven Bags with Production and Cost Benefits
Our non-woven bags stand out in the market. The production is fully automated, enabling us to offer bags in various styles and colors to suit different preferences. Our own fabric production and efficient PP sourcing give us a cost edge. By choosing us, you can benefit from these advantages. Contact Mandy on Whatsapp: +86 13599755808 for a complimentary sample. Don’t miss the chance to place an order with great discounts.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for your comment! Glad you brought up your doubts. Care to share what specifically seemed off or unclear? We’re always looking to improve and clarify.