Introduction
Nonwoven fabrics have emerged as versatile materials that bridge functionality and innovation across a myriad of industries. Unlike traditional woven textiles, nonwoven fabrics are produced through processes that bond fibers together via mechanical, thermal, or chemical methods, resulting in a fabric that can provide unique properties tailored to specific applications. This distinction makes nonwoven fabrics a preferable choice for manufacturers seeking efficient, cost-effective solutions without compromising quality.
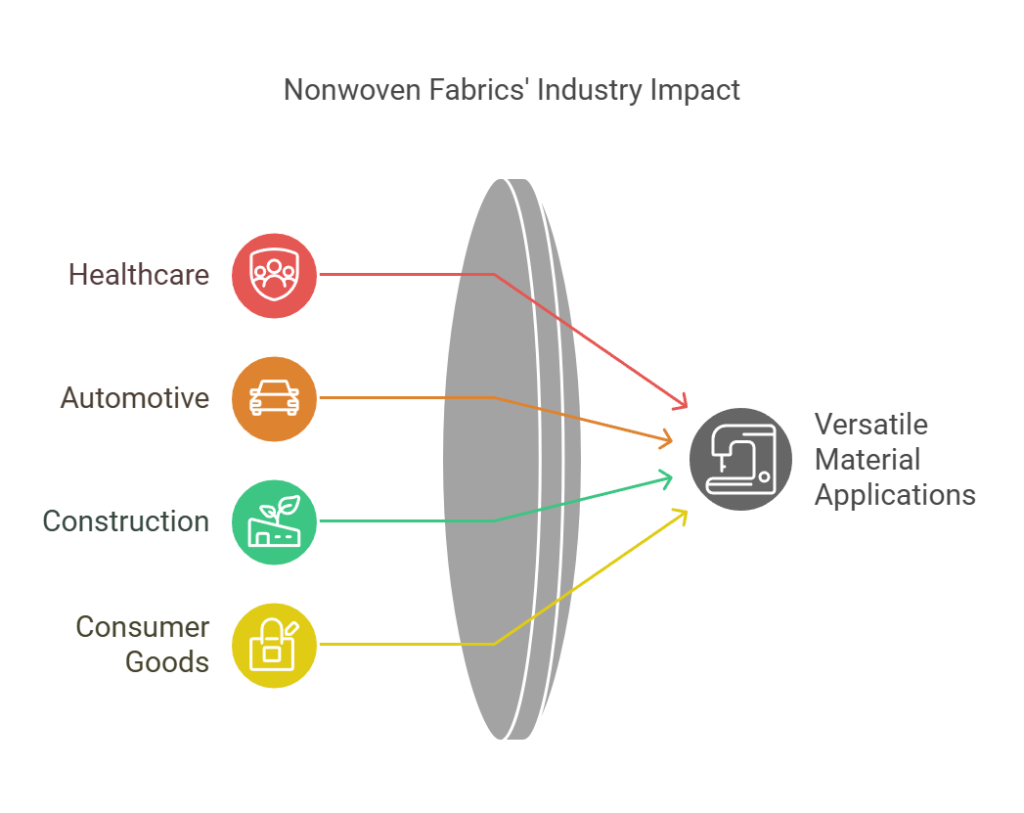
The significance of nonwoven fabrics has expanded tremendously since their inception in the mid-20th century. Their lightweight, breathable, and durable characteristics have carved a niche in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, construction, and even consumer goods. In healthcare, for example, nonwoven materials are utilized for surgical gowns, masks, and sterilization wraps, providing both protection and comfort to medical professionals and patients alike. This illustrates the crucial role that nonwoven fabrics play in ensuring safety and hygiene in critical environments.
Furthermore, in the automotive industry, nonwoven fabrics are increasingly employed in soundproofing, insulation, and upholstery due to their customizable properties and ability to reduce weight, which ultimately enhances fuel efficiency. The construction sector benefits from nonwoven fabrics as well, particularly in geotextiles for erosion control and landscaping, highlighting how these materials contribute to sustainable building practices.
In conclusion, the diverse applications of nonwoven fabrics demonstrate their adaptability and importance in various fields, underscoring the ongoing innovation and development within this sector. As industries continue to evolve, the relevance of nonwoven fabrics is likely to increase, reflecting their capacity to meet changing demands and enhance overall functionality.
What are Nonwoven Fabrics?
Nonwoven fabrics are unique textile materials manufactured without the traditional weaving or knitting processes commonly used in fabric production. The manufacturing of nonwoven fabrics involves a variety of methods, primarily entailing the bonding of fibers through mechanical, chemical, or thermal means. This process allows for a wide range of applications due to the distinct characteristics of nonwoven materials.
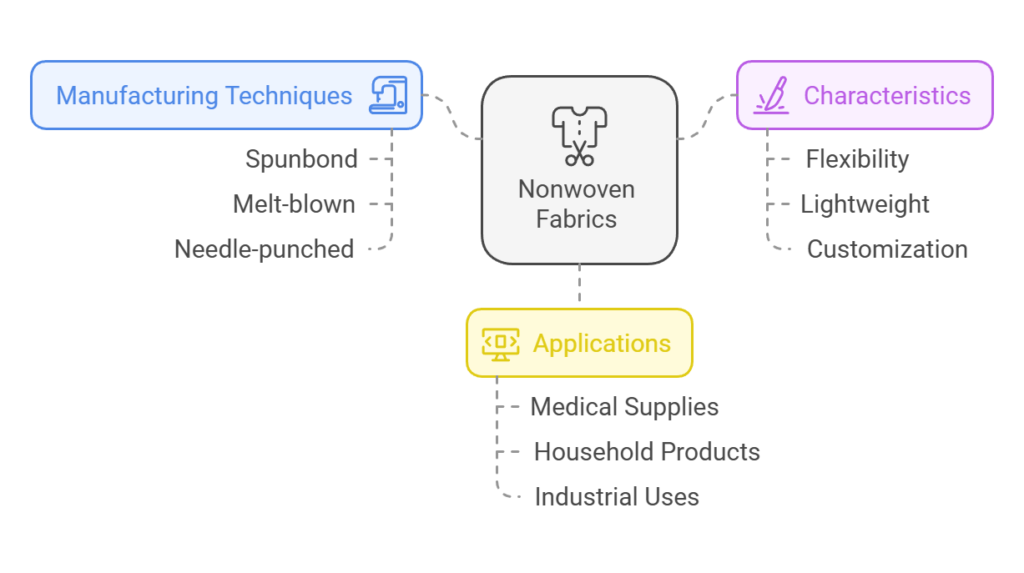
There are several categories of nonwoven fabrics, which can be classified based on their manufacturing technique. For instance, spunbond fabrics are created by extruding thermoplastic polymer fibers, which are then bonded together, while melt-blown fabrics involve the blowing of molten polymer through a high-velocity jet of air, resulting in a fine mesh. Moreover, needle-punched fabrics are formed by entangling fibers mechanically, providing excellent durability.
The primary distinction between nonwoven and woven fabrics lies in their structure. Woven fabrics are created by interlacing threads in a grid-like pattern, while nonwoven fabrics rely on fibrous layers that are either randomly arranged or laid in specified patterns. This characteristics endow nonwoven materials with high flexibility, lightweight properties, and the ability to be engineered for various purposes.
Furthermore, nonwoven fabrics exhibit several advantageous attributes, including breathability, absorbency, and insulation, making them suitable for diverse applications ranging from medical supplies to household products. Their versatility is underscored by the extensive customization options available, allowing manufacturers to tailor fabric properties such as thickness, strength, and texture to meet specific requirements.
Overall, nonwoven fabrics represent a significant innovation in textile engineering, offering a wide array of solutions in various industries. Their unique manufacturing processes and functional characteristics distinguish them from conventional woven fabrics, making them increasingly popular in today’s market.
Applications in Medical Industry
Nonwoven fabrics play a critical role in the medical industry, providing essential products that ensure hygiene, safety, and comfort. Their unique structure, composed of synthetic or natural fibers bonded together, gives them distinctive properties ideal for various applications. Among the most common uses of nonwoven fabrics in healthcare settings are surgical masks, gowns, and absorbent dressings, all of which contribute significantly to patient protection and infection control.
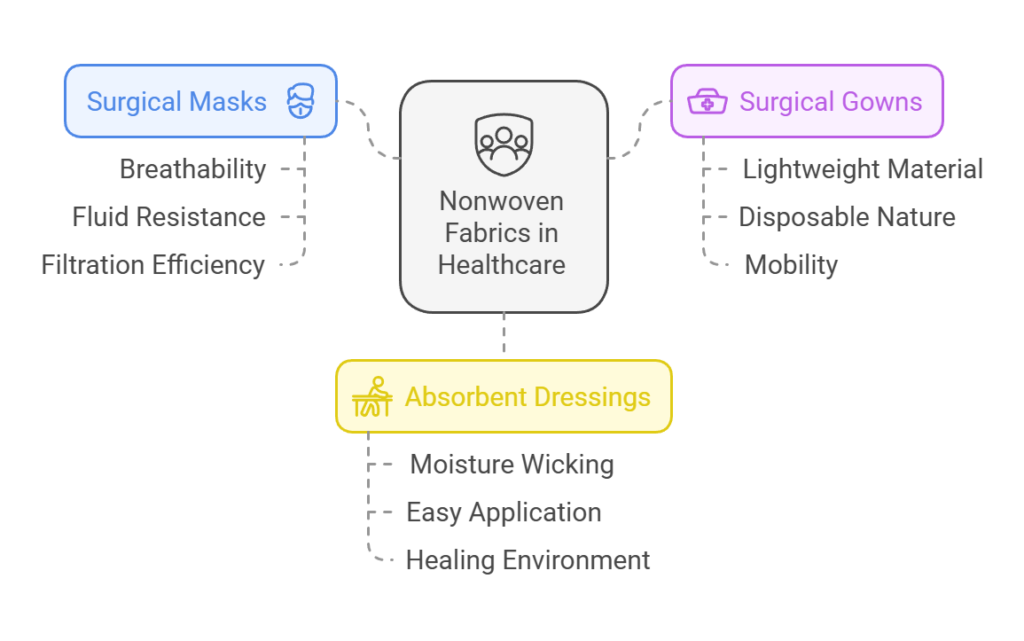
Surgical masks made from nonwoven materials are a vital barrier against pathogens. They offer breathability and fluid resistance, protecting healthcare professionals and patients during procedures. Their disposability reduces the risk of cross-contamination, making them an essential component of personal protective equipment (PPE). With advancements in medical technology, these masks have evolved to include various filtration efficiencies, ensuring enhanced protection against airborne particles and bacteria.
In addition to masks, nonwoven fabrics are widely used in surgical gowns. These gowns provide critical protection to both the patient and the healthcare provider by minimizing the risk of exposure to infectious agents. The lightweight and comfortable nature of nonwoven materials ensures that medical staff can perform their duties without compromising on mobility. The disposable nature of these gowns also contributes to their hygiene, as they can be discarded after a single use, further reducing the potential for infection.
Furthermore, absorbent dressings made from nonwoven fabrics are crucial in wound care management. Their ability to wick moisture away from the wound ensures a conducive healing environment while protecting against external contaminants. Nonwoven dressings are designed for easy application and removal, which assists in patient comfort and aids the healing process. With the continuous evolution of nonwoven technology, these medical applications continue to improve, reflecting the synthesis of functionality and innovation in modern healthcare.
Nonwovens in Construction and Building Materials
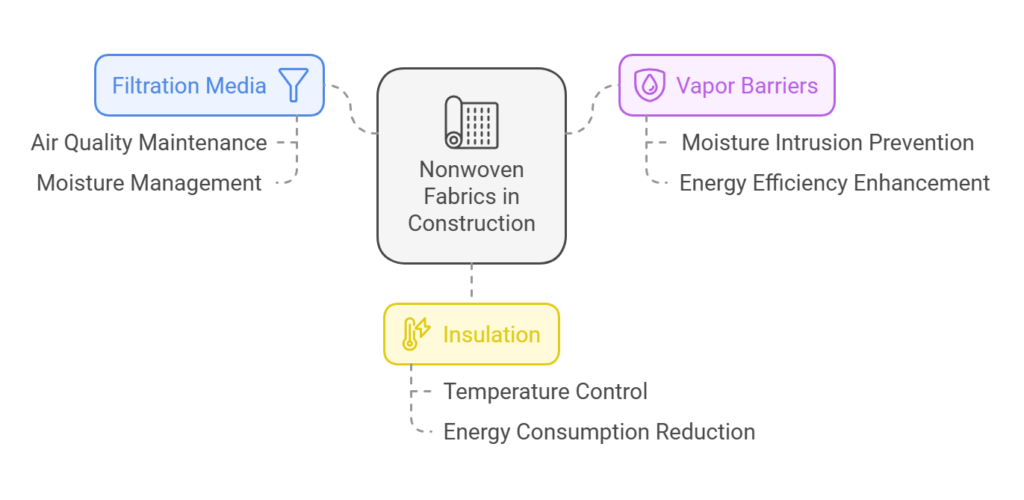
Nonwoven fabrics are gaining popularity in the construction industry due to their versatility and functional properties. These fabrics, composed of fibers that are bonded together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes, serve various critical roles as filtration media, vapor barriers, and insulation. Their utilization in these areas demonstrates their effectiveness in enhancing building performance and sustainability.
One significant application of nonwoven fabrics in construction is their use as filtration media. They are often integrated into air and water filtration systems, providing effective barriers that prevent the passage of debris, dust, and harmful particles. The porous structure of nonwovens allows for excellent liquid and air permeability, which is vital for maintaining air quality and managing moisture in buildings. Their ability to trap contaminants while allowing airflow makes them an ideal choice for HVAC systems and water drainage solutions.
Another important role is that of vapor barriers. Nonwoven fabrics act as a protective layer between building materials and the external environment, preventing moisture intrusion that can lead to mold growth and structural deterioration. The moisture resistance inherent in nonwovens ensures that insulation materials remain effective, thereby enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. This property is critical in regions with varying climates, where managing humidity levels is essential to preserving the integrity of the structure.
Additionally, nonwoven fabrics are utilized in insulation applications due to their lightweight and durable characteristics. They provide thermal resistance, helping to maintain temperature control within building envelopes. This efficiency not only contributes to occupant comfort but also reduces energy consumption, making nonwovens a sustainable option in modern construction methodologies.
In conclusion, nonwoven fabrics play a crucial role in construction and building materials, serving as effective filtration media, vapor barriers, and insulation. Their unique properties make them an indispensable component in enhancing both the functionality and sustainability of contemporary building practices.
The Role of Nonwoven Fabrics in Consumer Products
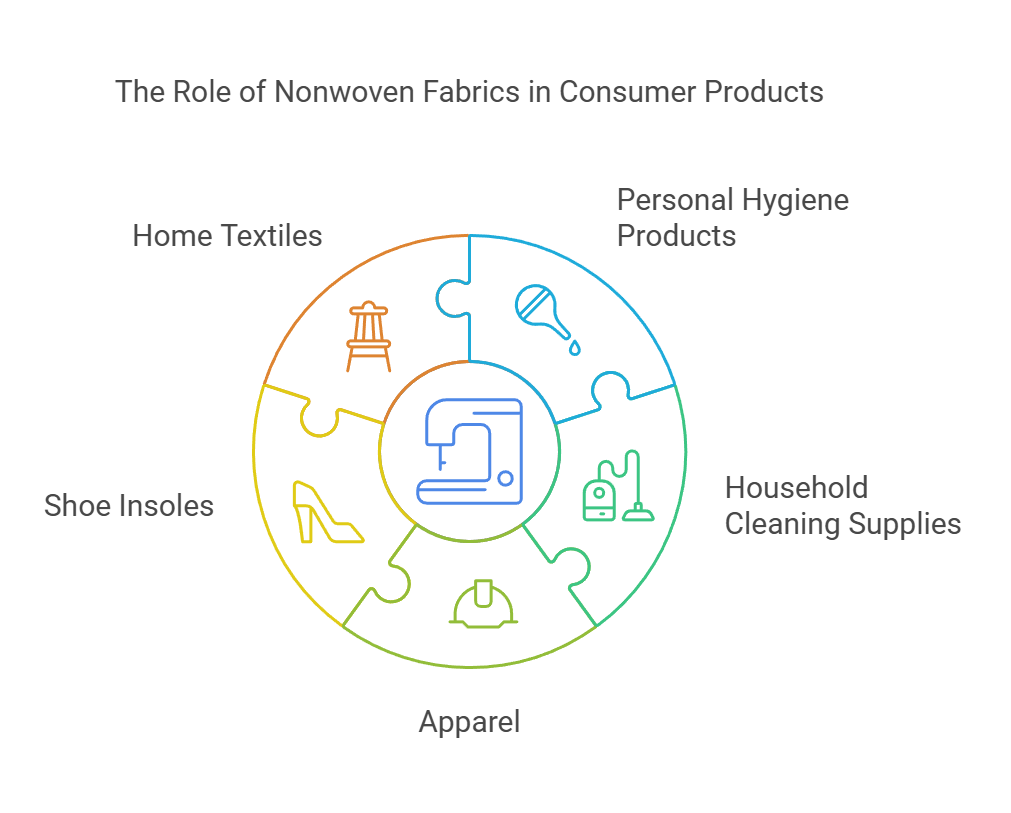
Nonwoven fabrics play a pivotal role in the design and functionality of various consumer products that we encounter daily. These textiles are characterized by their unique structure, which is produced by bonding fibers together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes, rather than weaving or knitting. As a result, nonwoven fabrics offer distinct advantages that enhance product performance and user experience across a range of applications.
One of the most notable uses of nonwoven fabrics can be found in personal hygiene products such as diapers and feminine hygiene items. In diapers, the incorporation of nonwoven layers ensures excellent absorbency, breathability, and comfort for infants. Nonwovens serve as topsheets that wick moisture away from the skin while preventing leaks, thereby keeping the surface dry and reducing the risk of irritation. Similarly, in feminine hygiene products, nonwoven materials are used to create soft, comfortable linings that maintain high absorbency while facilitating discretion and ease of use.
Beyond personal hygiene, nonwoven fabrics play an important role in household cleaning supplies. Products such as cleaning wipes benefit from nonwovens due to their durability and ability to trap dirt and grime effectively. The engineered structure of these fabrics allows for efficient liquid retention and quick-drying properties, making them suitable for various cleaning tasks. Moreover, nonwoven disposable cleaning cloths contribute significantly to convenience as they provide a single-use option that can effectively replace traditional cloths, reducing laundry loads.
In addition to these applications, nonwoven fabrics are utilized in other consumer products, including apparel, shoe insoles, and home textiles. Their versatility not only enhances the performance of these products but also supports innovative designs that align with consumer preferences. As the market for nonwoven fabrics continues to grow, their role in diverse consumer products will undoubtedly expand, further improving functionality and user satisfaction.
Innovative Uses in Agriculture
Nonwoven fabrics have emerged as a vital resource in the agricultural sector, enabling various applications that contribute significantly to crop production and sustainability. One of the primary uses of nonwoven fabrics in agriculture is for crop protection. These fabrics provide a lightweight, protective barrier that safeguards plants from harsh environmental conditions and pests. For instance, nonwoven row covers can shield seedlings from frost, while simultaneously enhancing sunlight penetration, thereby promoting better growth during adverse weather conditions.
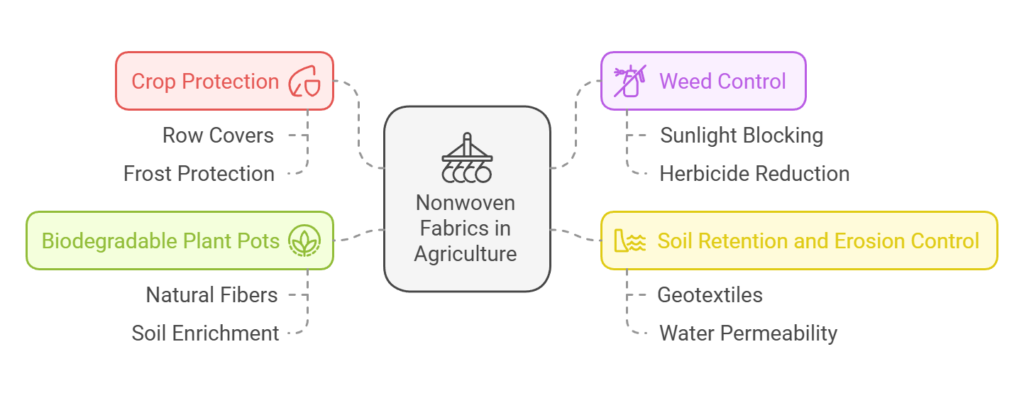
Moreover, nonwoven materials are often utilized for weed control. Their unique structure prevents sunlight from reaching weed seeds, inhibiting germination and subsequently reducing the need for chemical herbicides. This natural method of weed management not only supports environmental sustainability but also improves soil health by minimizing chemical runoff, which can be detrimental to surrounding ecosystems.
In addition to pest management and weed control, nonwoven fabrics are beneficial for soil retention and erosion control. By applying nonwoven geotextiles, farmers can stabilize the soil, preventing erosion caused by wind and water. These fabrics allow for water permeability while maintaining soil integrity, thus enhancing water conservation efforts. Furthermore, they encourage aeration and drainage, factors crucial for root development, leading to improved overall plant health and productivity.
Another innovative application of nonwoven fabrics in agriculture is in the production of biodegradable plant pots. These pots, made from natural fibers, provide a sustainable alternative to plastic containers, offering an eco-friendly solution that can decompose in the soil, ultimately enriching it. Such advancements demonstrate how nonwoven fabrics facilitate various agricultural practices, fostering efficiency and promoting a healthier environment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics offer a unique array of applications, but their environmental impact merits a thorough examination. A significant advantage of nonwoven materials is their potential to reduce waste compared to traditional textiles. For instance, nonwovens can be produced with minimal processing, which often translates to lower energy consumption and fewer chemicals used during manufacturing. Many nonwoven fabrics are made from recyclable materials, further enhancing their sustainable credentials. Additionally, the lifecycle of these fabrics can be optimized, following principles of circular economy, helping to minimize waste.
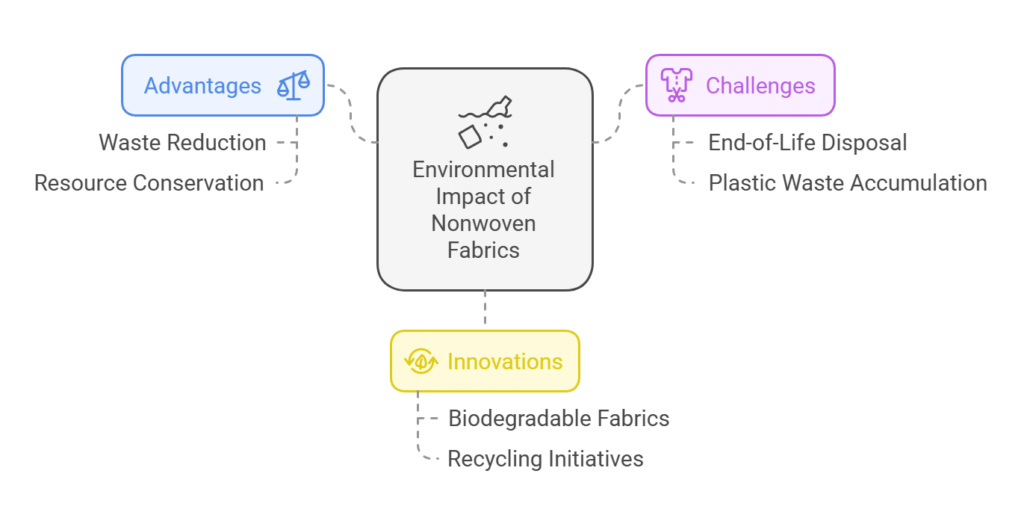
However, while nonwoven fabrics have attributes that are beneficial to the environment, they also present challenges, particularly concerning end-of-life disposal. As many nonwovens are made from synthetic fibers, they may not biodegrade as readily as natural textiles, leading to the potential accumulation of plastic waste in landfills. This situation raises concerns regarding pollution and sustainability. Consequently, there is an ongoing dialogue within the industry on how best to address these challenges through innovation.
Advancements in sustainable materials are becoming increasingly prevalent. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop biodegradable nonwoven fabrics that comply with environmental regulations while maintaining performance standards. Additionally, numerous recycling initiatives are emerging, aimed at ensuring that nonwoven products can be effectively reprocessed after their initial use. For example, certain nonwoven materials can now be repurposed into new products, reducing the demand for virgin materials and fostering a more sustainable cycle.
In summary, while nonwoven fabrics hold promise for reducing waste and conserving resources, their environmental impact is multi-faceted. Continued innovation and commitment to sustainability practices are essential to improve their end-of-life solutions, ensuring a more environmentally friendly pathway in the textile industry.
Future Trends in Nonwoven Fabric Technology
The nonwoven fabric industry is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology, materials, and production processes. One of the most significant trends reshaping this sector is the adoption of eco-friendly and sustainable materials in manufacturing. As environmental concerns become increasingly prominent, manufacturers are focusing on biodegradable and recyclable options. This shift not only caters to consumer demand for sustainable products but also aligns with global regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting greener alternatives.
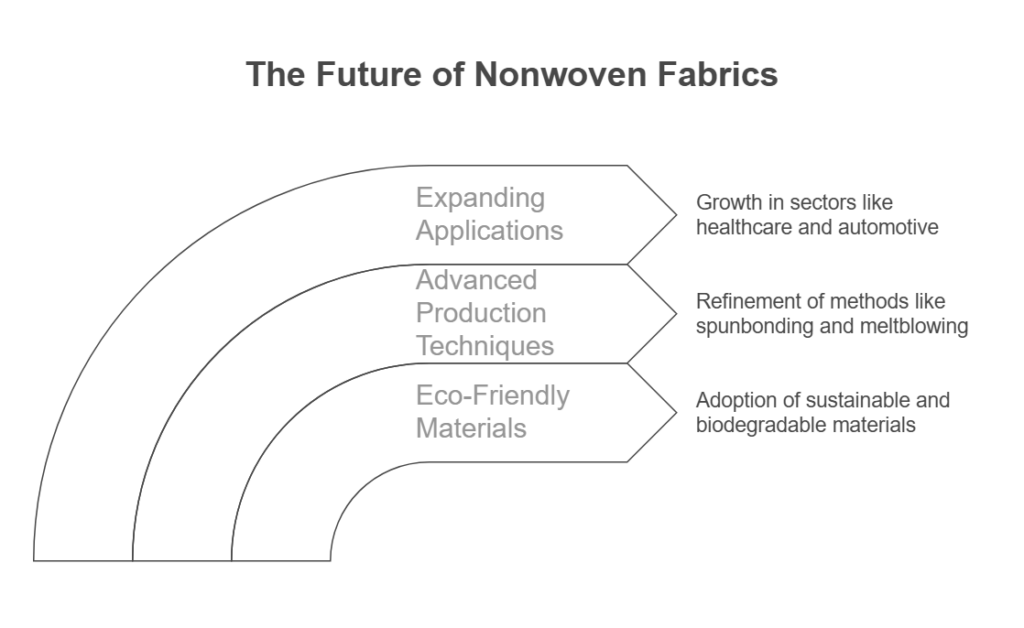
Additionally, advancements in production technologies are enhancing the efficiency and versatility of nonwoven fabrics. Techniques such as spunbonding, meltblowing, and impregnated nonwovens are being refined, allowing for greater customization in terms of texture, strength, and absorbency. These innovations contribute to the development of high-performance nonwovens suitable for a multitude of applications ranging from medical to automotive. For example, the growth in the healthcare sector is prompting the creation of specialized nonwovens that offer improved barrier properties, fluid management, and comfort.
Moreover, the expansion of nonwoven fabrics into emerging markets is an accelerating trend. Sectors such as hygiene, filtration, and construction are increasingly utilizing nonwoven technology due to its cost-effectiveness and adaptability. The automotive industry, in particular, is embracing nonwovens for sound insulation, lightweight components, and interior linings. As industries seek innovative solutions to enhance product performance while maintaining cost efficiency, nonwoven fabrics are poised for extensive integration into diverse applications.
In conclusion, the future of nonwoven fabric technology is bright, characterized by sustainable practices, advanced production techniques, and versatile applications across various sectors. This progression will likely reinforce nonwoven fabrics’ position as a vital component across multiple industries, catering to both functional and environmental needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Nonwoven fabrics have gained considerable attention across various industries due to their unique properties and applications. Below are some common questions and answers that can help clarify essential aspects of nonwoven fabrics.
Are nonwoven fabrics safe for use? Yes, nonwoven fabrics are generally considered safe. They are produced from polymers, such as polypropylene and polyester, that can be non-toxic and hypoallergenic. Many nonwoven applications, particularly in hygiene products like diapers and medical garments, prioritize safety and regulatory compliance to ensure they are safe for their intended users.
How cost-effective are nonwoven fabrics compared to traditional fabrics? Nonwoven fabrics often prove to be more cost-effective than traditional woven or knitted fabrics. The manufacturing processes of nonwoven fabrics can be less labor-intensive and can utilize fewer resources, leading to lower production costs. Additionally, their durability and versatility enhance their value, making them a preferred choice for many industries, from medical to automotive.
How do nonwoven fabrics compare with other fabric types? Nonwoven fabrics differ significantly from woven and knitted fabrics in terms of structure and properties. Unlike woven fabrics, which are created by weaving threads together, nonwoven fabrics are formed directly from fibers through processes such as bonding or entanglement. This characteristic results in unique attributes, such as improved filtration capabilities and better resistance to liquids. Furthermore, nonwoven fabrics can be engineered to meet specific requirements, making them adaptable for diverse applications.
In summary, nonwoven fabrics offer numerous advantages, including safety, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Understanding these features can help consumers and industry professionals make informed decisions regarding the use of nonwoven materials in their respective fields.
8 Responses
Your writing is not only informative but also incredibly inspiring. You have a knack for sparking curiosity and encouraging critical thinking. Thank you for being such a positive influence!
Thank you for your kind words! Glad you found it useful. 😊
Blue Techker very informative articles or reviews at this time.
Thanks for your comment! Glad you find our articles informative.
Noodlemagazine naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Thank you so much for your kind words about our website. We sincerely apologize for the spelling issues. Our team will promptly review and correct the posts. Appreciate your understanding and looking forward to your next visit.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
We’re thrilled to hear that our article was helpful to you! We do have more related content. You can explore our “Industry Insights” section on the website, where we regularly publish in – depth articles on non – woven materials, applications, and the latest trends. Also, subscribe to our newsletter on the homepage to get notified of new posts directly in your inbox.
Thank you for your interest!