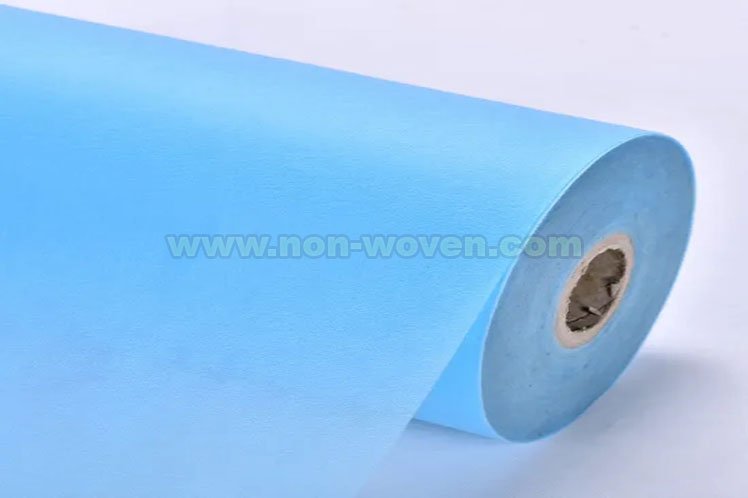
What is Nonwoven Cloth?
Nonwoven cloth is a fabric-like material crafted from staple fibers (short) and long fibers (continuous long), which are bonded together through various methods such as chemical, mechanical, heat, or solvent treatment. Unlike traditional woven or knitted fabrics, nonwoven cloth does not involve weaving or knitting processes. Its production involves layering fibers in a random or oriented manner, followed by a bonding process to create a cohesive material.

There are several types of nonwoven cloth, each distinguished by its manufacturing process and application. For instance, spunbond nonwoven cloth is created by extruding thermoplastic fibers, which are then laid onto a conveyor belt and bonded together using heat or chemical treatments. Meltblown nonwoven cloth, on the other hand, is made by extruding melted polymer fibers through small nozzles and blowing them onto a conveyor belt to form a web, which is then bonded. Other types of nonwoven cloth include needle-punched, hydroentangled, and thermal-bonded nonwovens, each with its specific method of production and unique properties.
One of the defining characteristics of nonwoven cloth is its versatility. It can be engineered to exhibit a range of properties such as durability, flexibility, absorbency, and resilience. This adaptability makes nonwoven cloth suitable for a wide array of applications across various industries. In healthcare, nonwoven cloth is used for surgical gowns, masks, and disposable gloves due to its sterility and barrier properties. In agriculture, it serves as crop covers and weed control fabrics. The automotive industry utilizes nonwoven materials for insulation, filtration, and upholstery. Moreover, the fashion industry leverages nonwoven cloth for items like disposable garments and accessories.
The combination of advanced manufacturing techniques and the inherent properties of nonwoven cloth has led to its widespread adoption and continued innovation, making it an indispensable material in numerous sectors.
Common Uses and Applications of Nonwoven Cloth
Nonwoven cloth, a versatile and adaptable material, finds extensive applications across a multitude of industries. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for various products, especially in the medical field, agriculture, automotive sector, and household items.

In the medical domain, nonwoven cloth is indispensable. It is widely used in the production of surgical gowns, masks, and sanitary napkins. These materials are chosen for their breathability, liquid resistance, and ability to provide a sterile barrier, crucial in medical environments. For instance, surgical masks made from nonwoven cloth have been instrumental in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, offering both filtration efficiency and comfort to healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The agricultural industry also benefits significantly from nonwoven cloth. Its use in crop protection and soil stabilization is well-documented. Nonwoven fabrics act as protective covers for crops, shielding them from pests, extreme weather conditions, and weeds, thus enhancing crop yield and quality. Additionally, these materials are employed in soil stabilization projects to prevent erosion and improve soil structure, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
In the automotive sector, nonwoven cloth plays a crucial role in enhancing vehicle comfort and performance. It is used in car interiors, providing sound insulation, cushioning, and aesthetic appeal. Moreover, nonwoven fabrics are integral in the manufacturing of filters and insulation materials, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of vehicles. For example, air filters made from nonwoven cloth ensure clean air circulation within the car, enhancing the driving experience.
Household products are another area where nonwoven cloth demonstrates its versatility. Items such as wipes, filters, and geotextiles are commonly made from nonwoven fabrics. These products benefit from the material’s high absorbency, durability, and ease of production. Geotextiles, in particular, are used in construction projects for drainage, filtration, and reinforcement, showcasing the broad applicability of nonwoven cloth in everyday life.
In conclusion, the diverse applications of nonwoven cloth across various industries underscore its importance and adaptability. From medical products to agricultural solutions, automotive components to household items, nonwoven fabrics offer practical and efficient solutions, making them an essential material in modern manufacturing and daily life.
Benefits and Advantages of Using Nonwoven Cloth
Nonwoven cloth has emerged as a material of choice in various industries due to its numerous advantages over traditional woven fabrics. One of the primary benefits is its cost-effectiveness. The production process of nonwoven cloth is generally less labor-intensive and quicker, reducing overall manufacturing costs. This economic advantage makes it an attractive option for large-scale applications, from industrial use to consumer products.

Another significant benefit of nonwoven cloth is its lightweight nature. This feature not only makes it easy to handle and transport but also contributes to reduced shipping costs and lower carbon footprints. Industries such as automotive and furniture manufacturing have capitalized on this property, integrating nonwoven materials to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs.
High absorbency is another notable characteristic of nonwoven cloth. This makes it particularly suitable for medical and hygiene products, such as surgical gowns, masks, diapers, and sanitary napkins. Studies have shown that nonwoven fabrics can absorb up to ten times their weight in liquid, a property that is crucial for maintaining hygiene and comfort in medical and personal care products.
Furthermore, nonwoven cloth is often praised for its eco-friendly attributes. Many types are recyclable and biodegradable, contributing to environmental sustainability. For instance, nonwoven polypropylene fabrics can be recycled and repurposed, reducing waste and conserving resources. The biodegradability of certain nonwoven materials also ensures that they break down more easily in landfills, lessening their environmental impact.
Research supports these benefits, with findings indicating that the global nonwoven fabric market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the material’s versatility and the advantages it offers across various sectors, including healthcare, automotive, construction, and agriculture.
In conclusion, the benefits and advantages of nonwoven cloth—ranging from cost-effectiveness and lightweight properties to high absorbency and eco-friendliness—contribute to its growing popularity and adoption across multiple industries. As research and technological advancements continue to enhance its properties, nonwoven cloth is likely to become even more integral to modern manufacturing and consumer products.
Future Trends and Innovations in Nonwoven Cloth
The nonwoven cloth industry stands at the cusp of transformative change, driven by continuous research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the properties and applications of nonwoven fabrics. One of the most promising areas of innovation is the integration of smart textiles. These intelligent materials are designed to respond to environmental stimuli, such as changes in temperature or moisture levels, thereby offering enhanced functionality for a variety of applications, including medical textiles, wearable technology, and home furnishings.

Nanotechnology is another groundbreaking advancement making significant inroads in the nonwoven cloth sector. By incorporating nanoparticles into nonwoven fabrics, manufacturers are able to impart unique properties such as antimicrobial resistance, increased strength, and improved filtration capabilities. These enhancements are particularly valuable in healthcare settings where hygiene and durability are paramount, as well as in industrial applications requiring high-performance materials.
Sustainability trends are also reshaping the future of nonwoven fabrics. With increasing awareness of environmental issues, there is a growing demand for biodegradable and eco-friendly nonwoven materials. Researchers are developing innovative solutions such as bio-based polymers and recyclable nonwoven fabrics to reduce the ecological footprint of these products. These advancements are not only beneficial for the environment but also align with consumer preferences for sustainable products, thereby driving market growth.
The nonwoven cloth market is poised for significant expansion, with emerging applications in sectors such as automotive, construction, and agriculture. For instance, nonwoven fabrics are being utilized for car interiors, insulation materials, and crop protection, highlighting their versatility and broadening the scope of their use. Industry experts forecast robust growth, driven by technological advancements and the increasing adoption of nonwoven solutions across various industries.
Insights from industry leaders underscore the potential for continued innovation and market expansion. As the nonwoven cloth industry evolves, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in meeting the demands of modern technology and sustainability, ensuring its relevance and indispensability in the years to come.