Introduction: What are Nonwoven Innovations?
Nonwoven innovations represent a transformative segment within the fabric technology landscape. Unlike traditional woven or knitted materials, nonwoven fabrics are produced through alternative methods such as bonding fibers together using chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes. This unique production technique allows for the creation of materials with distinct properties, tailored to meet specific needs across various industries.
Nonwoven fabrics are engineered for performance and versatility. Their applications span from medical textiles, including surgical gowns and face masks, to consumer goods such as wipes and hygiene products. The significance of nonwoven innovations lies in their ability to offer cost-effective, durable, and highly functional solutions compared to traditional fabrics. These materials can be designed to be lightweight, breathable, and strong, making them ideal for use in critical environments where reliability is paramount.
The rising importance of nonwoven fabrics is also driven by their contribution to sustainability. Many nonwoven materials are designed to be biodegradable or recyclable, addressing growing environmental concerns. Additionally, the production processes for nonwovens often consume less energy and produce fewer emissions than conventional textile manufacturing methods, further enhancing their appeal in an eco-conscious marketplace.
As technological advancements continue to evolve, nonwoven innovations are pushing the boundaries of what fabrics can achieve. Research and development in this field are leading to the creation of materials with enhanced properties, such as improved filtration efficiency, increased softness, and greater absorbency. These developments not only meet the challenges of modern applications but also open new possibilities for future use cases.
This blog post will delve deeper into the various aspects of nonwoven innovations, examining their impact on different sectors and exploring the future potential of these groundbreaking materials. By understanding the fundamentals of nonwoven fabrics, readers can appreciate the significant role they play in the advancement of fabric technologies.
Answering the Big Question: Why are Nonwoven Innovations Important?
Nonwoven innovations are pivotal in the modern fabric industry due to their multifaceted advantages, which include cost-effectiveness, versatility, and ecological benefits. These materials, produced through methods such as chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes, offer a more economical alternative to traditional woven fabrics. The absence of weaving or knitting significantly reduces production time and costs, making nonwoven fabrics an attractive option for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Versatility is another critical factor that underscores the importance of nonwoven innovations. These fabrics can be engineered to possess specific properties such as absorbency, resilience, softness, and strength, catering to a wide range of applications. From medical supplies like surgical masks and gowns to everyday products such as wipes and filters, nonwoven fabrics meet diverse needs across various industries. This adaptability ensures that nonwoven technologies continue to evolve, addressing emerging demands and challenges effectively.
Moreover, nonwoven innovations contribute significantly to environmental sustainability. Many nonwoven materials are designed to be biodegradable or recyclable, reducing the ecological footprint associated with fabric production and disposal. The use of renewable resources and eco-friendly production processes further enhances the green credentials of nonwoven fabrics. By incorporating sustainable practices, the nonwoven industry aligns with global efforts to mitigate environmental impact and promote a circular economy.
In conclusion, the importance of nonwoven innovations lies in their ability to provide cost-effective, versatile, and environmentally sustainable fabric solutions. As the demand for efficient and eco-friendly materials continues to rise, nonwoven technologies stand at the forefront, driving progress and innovation in the fabric industry.
The Evolution of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics, a pivotal innovation in textile manufacturing, have a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations. The earliest instances of nonwoven materials can be traced to ancient Egypt, where felt, one of the oldest known nonwoven fabrics, was widely utilized. However, the modern development of nonwoven fabrics began in the early 20th century, catalyzed by advancements in synthetic fibers and industrial processes.
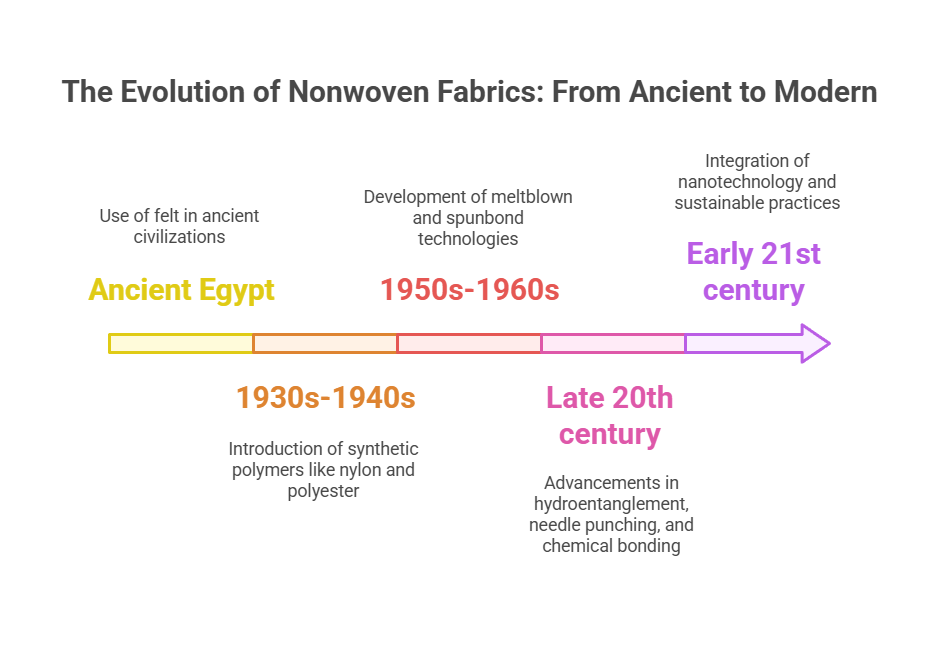
The 1930s and 1940s marked significant milestones in the evolution of nonwoven technologies. During this period, the introduction of synthetic polymers such as nylon and polyester laid the groundwork for the development of more durable and versatile nonwoven fabrics. These synthetic fibers offered superior properties compared to natural fibers, including enhanced strength, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the nonwoven industry saw a surge in innovation and commercialization. The development of meltblown and spunbond technologies revolutionized the production of nonwoven fabrics, enabling the creation of fine, continuous filaments that could be bonded together without weaving or knitting. These advancements facilitated the mass production of nonwoven materials, making them accessible for a wide range of applications, from medical textiles to automotive components.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries have witnessed continuous advancements in nonwoven fabric technologies. Innovations such as hydroentanglement, needle punching, and chemical bonding have further diversified the types of nonwoven fabrics available. Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology and sustainable practices has led to the development of eco-friendly nonwovens that meet the growing demand for sustainable and biodegradable materials.
Today, nonwoven fabrics are an integral part of numerous industries, including healthcare, agriculture, construction, and fashion. The evolution of nonwoven technologies continues to drive innovation, offering new possibilities for creating high-performance, cost-effective, and sustainable materials. As we look to the future, ongoing research and development in this field promise to further expand the applications and capabilities of nonwoven fabrics, solidifying their role in the fabric technologies of tomorrow.
Key Technologies Driving Nonwoven Innovations
The nonwoven fabric industry is undergoing a transformative phase, propelled by key technological advancements that are reshaping its landscape. One of the most significant drivers of this innovation is developments in materials science. Advanced polymers and biopolymers are being utilized to create nonwoven fabrics with enhanced properties such as increased durability, flexibility, and biodegradability. These materials offer superior performance while also addressing environmental concerns, making them a critical component of sustainable fabric technologies.
Another pivotal technology is the evolution of manufacturing processes. Methods such as meltblown, spunbond, and hydroentangling are being optimized to produce nonwoven fabrics with refined textures and improved functional characteristics. The integration of nanotechnology in these processes has led to the creation of nanofibers that provide exceptional filtration and barrier properties. These innovations are particularly relevant in industries such as healthcare, where nonwoven fabrics are used for medical gowns, masks, and other critical protective gear.
Digital technologies are also playing a crucial role in driving nonwoven innovations. Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms are being deployed to streamline production processes, enhance quality control, and reduce waste. The use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in manufacturing facilities is enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, resulting in more efficient and reliable production lines. Additionally, digital platforms are facilitating greater customization and faster prototyping, allowing manufacturers to meet specific customer requirements with greater agility.
The convergence of these technologies is not only enhancing the performance and versatility of nonwoven fabrics but also expanding their application scope. From automotive interiors to personal hygiene products, the advancements in materials science, manufacturing processes, and digital integration are setting new standards in the industry. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to unlock even more innovative solutions, driving the future of nonwoven fabric technologies forward.
Applications of Nonwoven Fabrics Across Industries
Nonwoven fabrics have become integral across various industries, showcasing their versatility and adaptability. One of the most prominent sectors utilizing nonwoven fabrics is healthcare. For instance, nonwoven surgical masks and gowns are essential in maintaining hygiene and preventing infection during medical procedures. The fabric’s ability to provide a barrier against bacteria and viruses while remaining breathable and comfortable makes it an ideal choice. Additionally, nonwoven fabrics are used in wound dressings and disposable medical supplies, contributing significantly to patient care and safety.
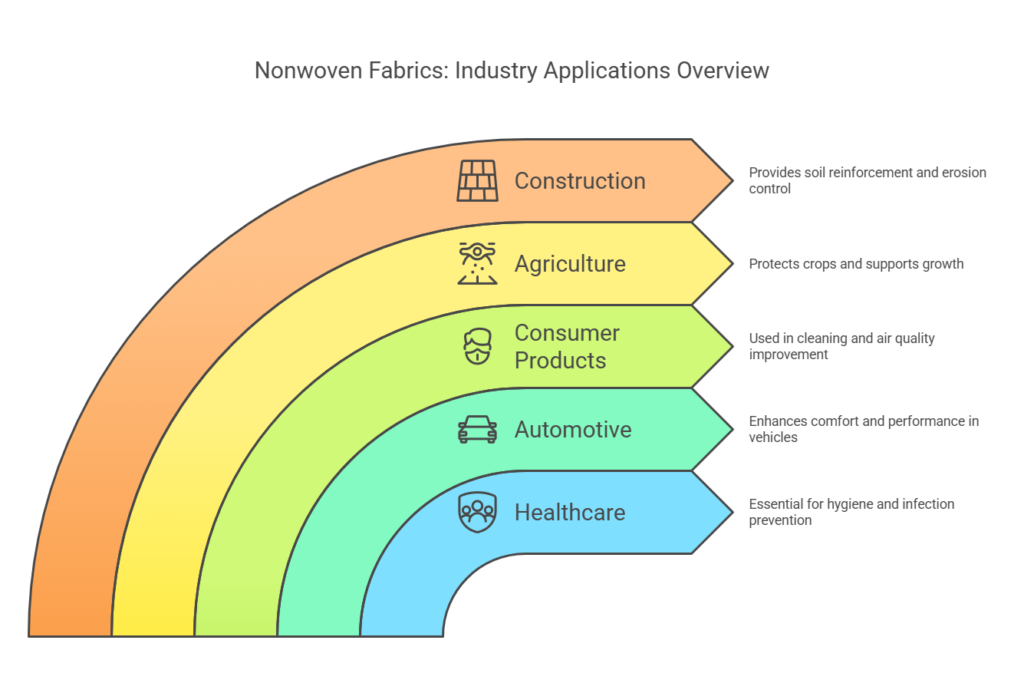
In the automotive industry, nonwoven fabrics have found numerous applications, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. Interior linings, such as headliners, carpets, and door panels, frequently incorporate nonwoven materials. These fabrics offer excellent sound insulation, lightweight properties, and durability, improving the vehicle’s overall performance and passenger comfort. Furthermore, nonwoven fabrics are used in automotive filters, where their high filtration efficiency ensures clean air circulation within the vehicle, thus maintaining a healthier environment for occupants.
Consumer products are another domain where nonwoven fabrics are extensively utilized. Household wipes, for example, leverage the absorbent nature of nonwoven materials to provide effective cleaning solutions. These wipes are designed for various purposes, including surface cleaning, personal hygiene, and even industrial applications. Nonwoven fabrics are also employed in producing filters for air purifiers and vacuum cleaners, where their fine fibers trap dust and allergens, enhancing indoor air quality.
The flexibility of nonwoven fabrics extends beyond these industries, finding niches in agriculture, construction, and fashion. Agricultural covers made from nonwoven materials protect crops from pests and extreme weather, promoting healthier growth. In construction, geotextiles reinforce soil and provide erosion control, contributing to infrastructure stability. Fashion designers are increasingly exploring nonwoven fabrics for their innovative textures and sustainable attributes, pushing the boundaries of traditional textile design.
The myriad applications of nonwoven fabrics underscore their importance in modern manufacturing and consumer goods. Their unique properties and diverse uses highlight the potential for further innovation and expansion in various industrial sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have garnered significant attention due to their versatile applications and potential for sustainable practices. A key environmental advantage of nonwoven fabrics is their capacity for biodegradability. Many nonwoven materials are designed to decompose naturally, reducing their long-term impact on landfills. For instance, nonwovens made from natural fibers like cotton, flax, and bamboo can break down more readily compared to traditional synthetic fabrics, contributing to a reduction in persistent waste.

In addition to biodegradability, the recycling processes for nonwoven fabrics are evolving. Advanced recycling techniques enable the recovery of fibers from used nonwoven products, which can then be repurposed into new materials. This closed-loop system minimizes waste and conserves resources, aligning with the principles of a circular economy. Companies are investing in innovative recycling technologies that can process a broader range of nonwoven materials, thereby enhancing the overall sustainability of the industry.
Eco-friendly manufacturing techniques are also playing a crucial role in the sustainability of nonwoven fabrics. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting methods that reduce energy consumption and minimize the release of harmful emissions. For example, water-based bonding agents and mechanical entanglement processes are being utilized to create nonwoven fabrics without the need for chemical adhesives, resulting in lower environmental impact. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities is gaining traction, further reducing the carbon footprint associated with nonwoven fabric manufacturing.
However, there are challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize the sustainability potential of nonwoven fabrics. One significant issue is the reliance on petroleum-based synthetic fibers, which are not biodegradable and pose environmental hazards. Transitioning to bio-based alternatives and improving the efficiency of recycling systems for synthetic nonwovens are critical steps towards mitigating these challenges. Moreover, educating consumers and industries about the environmental benefits and proper disposal methods of nonwoven products is essential in promoting sustainable practices.
Overall, while nonwoven fabrics offer promising pathways towards sustainability, continuous innovation and collaborative efforts are imperative to overcome existing challenges and enhance their environmental impact.
Future Trends in Nonwoven Innovations
The nonwoven fabric industry is on the brink of significant transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements and emerging applications. As we look ahead, several key trends are poised to redefine the landscape of nonwoven innovations. One of the most prominent trends is the integration of smart textiles, which merge traditional fabric properties with electronic capabilities. This innovation is expected to pave the way for intelligent, responsive fabrics used in healthcare, sportswear, and even military applications.
Another trend gaining traction is the development of sustainable nonwoven materials. With increasing environmental concerns, the industry is shifting towards eco-friendly alternatives, such as biodegradable and recyclable nonwovens. These materials not only reduce the environmental footprint but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. Companies are investing in research and development to create nonwovens from renewable resources, such as plant-based fibers and bio-polymers, which promise to revolutionize the market.
Moreover, advancements in nanotechnology are enabling the production of nonwoven fabrics with enhanced functionalities. Nanofibers, characterized by their high surface area and unique properties, are being incorporated into nonwoven materials to provide superior filtration, antimicrobial resistance, and improved mechanical strength. These attributes open up new possibilities for nonwovens in sectors such as medical, automotive, and construction industries, where performance and durability are paramount.
Market growth forecasts for the nonwoven fabric industry remain optimistic, with robust demand anticipated across various sectors. The healthcare industry, in particular, is expected to witness significant growth due to the increasing need for personal protective equipment (PPE) and medical textiles. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and home delivery services is driving the demand for nonwoven packaging solutions, which offer lightweight, cost-effective, and sustainable options.
As ongoing innovations continue to shape the future of nonwoven fabrics, the industry is set to experience a period of dynamic evolution. The convergence of technology and sustainability will likely drive the next wave of breakthroughs, positioning nonwoven fabrics as a critical component in the fabric technology landscape.
FAQs about Nonwoven Innovations
What are nonwoven fabrics?
Nonwoven fabrics are textile materials made from fibers bonded together through chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes rather than being woven or knitted. These fabrics are highly versatile and can be engineered for a wide range of applications, from medical textiles to geotextiles and automotive components.
How are nonwoven fabrics made?
The production of nonwoven fabrics typically involves processes such as spunbonding, meltblowing, and needle punching. In spunbonding, polymer filaments are extruded, stretched, and laid into a web, which is then bonded. Meltblowing involves extruding molten polymer through fine nozzles, creating microfibers that form a web. Needle punching mechanically entangles fibers using barbed needles to create a cohesive fabric.
What are the benefits of nonwoven fabrics?
Nonwoven fabrics offer numerous benefits, including high strength-to-weight ratios, breathability, and cost-effectiveness. They can be designed to be absorbent, water-resistant, or flame-retardant depending on the application’s requirements. Additionally, nonwoven fabrics often exhibit excellent filtration properties, making them ideal for medical and industrial uses.
Where are nonwoven fabrics commonly used?
Nonwoven fabrics are employed in a myriad of industries. Some common applications include disposable medical garments, hygiene products like diapers and sanitary pads, filtration systems, automotive interiors, and agricultural coverings. Their adaptability and customizability make them suitable for both single-use and durable products.
What innovations are driving the future of nonwoven fabrics?
Future innovations in nonwoven fabrics are being driven by advancements in material science and manufacturing technologies. Sustainable materials, such as biodegradable polymers and recycled fibers, are becoming increasingly popular. Additionally, smart textiles with embedded sensors and enhanced functionalities are being developed, broadening the scope of nonwoven applications in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and beyond.
Are nonwoven fabrics environmentally friendly?
The environmental impact of nonwoven fabrics depends on the materials and processes used in their production. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainability by utilizing eco-friendly raw materials and optimizing production methods to reduce waste and energy consumption. Biodegradable and recyclable nonwovens are at the forefront of this green innovation.
Can nonwoven fabrics be recycled?
Yes, many nonwoven fabrics can be recycled, depending on the type of fibers and bonding agents used. Recycling nonwovens involves collecting, sorting, and processing the materials to create new products. Advances in recycling technology are continually improving the efficiency and feasibility of recycling nonwoven fabrics, contributing to a more sustainable textile industry.

One Response
Thanks for your useful information about Nonwoven fabrics. These materials offer superior performance.