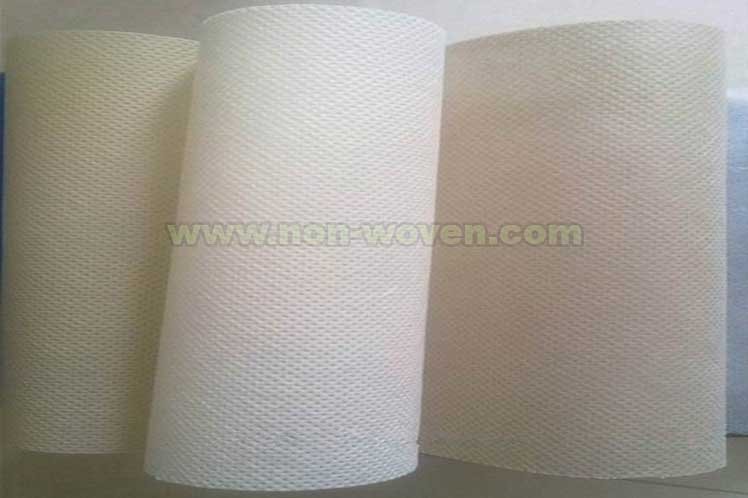
Introduction
Nonwoven fabric is created by bonding fibers together to create a fabric without the need for spinning or weaving. This process can be done using various methods, including mechanical, thermal, chemical, or adhesive bonding. Nonwoven fabric has many applications, from filtering to hygiene to home furnishings.
The following are ten nonwoven fabric examples that you’ll wish you knew about sooner.
Nonwoven Fabric in Disposable Wear:
Spunlaced nonwovens or “WaterJet” nonwovens are ideal for medical and personal care products due to their superior strength, absorbency, and softness. These fabrics are created by shooting high-pressure water jets onto a web of fibers and bonding them together through mechanical agitation. This process produces fabrics with a unique structure that adds strength and softness. Spunlaced nonwovens are also lightweight and breathable, making them an ideal choice for disposable wear and absorbent products. Needle-punched nonwovens are the most popular form of nonwoven fabrics used to create permanent clothing items. This type of fabric is created using a needle-punching machine to punch closely spaced felting needles through multiple layers of fibers. The needles create loops in the fabric that are then interlocked with other fibers, forming a highly durable fabric. Needle-punched nonwovens are also known for their superior strength and durability, making them an ideal choice for garments, upholstery, and medical fabrics.
Nonwoven Fabric in Industrial Uses:
Wet-laid nonwovens are commonly used in the automotive, transportation, and medical industries. This type of fabric is created by adding a binder chemical to a web of fibers and then mixing and blending the fibers into a slurry. The mixture is then mixed, stirred, and spread onto a forming belt, allowing the fibers to form a web. The web is then dried to form a fabric. The resulting fabric is superior in its strength and durability, making it ideal for automotive and transportation industries where a strong fabric is key. Melt-blown nonwovens are being increasingly used in industrial applications due to their unique properties. This type of fabric is created using a process where synthetic polymer fibers are extruded through small holes and onto a forming belt. The fibers are then melted and air-laid in a “web” pattern, creating a lightweight, breathable fabric. The structure of the fabric makes it ideal for use in filtration, protective clothing, and other industrial applications. Fibrous Network:
The use of chemical, mechanical, heat, or solvent treatment:
processes can also create highly absorbent nonwoven fabrics. This type of fabric is created by bonding together fibers to form a three-dimensional “network”. These fabrics are highly absorbent and can be used in a variety of applications including health care, filtration, and even industrial applications. Extrusion-coated nonwovens combine the strength of nonwoven fabrics with the durability of plastic films. This type of fabric is created by applying a lightweight plastic film onto a web of fibers and then bonding them together by extrusion. The resulting fabric is lightweight, breathable, and waterproof, making it ideal for use in automotive and protective garments.
Spunbonded Nonwovens:
Spunbonded nonwovens are created by taking extruded polymer fibers and melting them together. The fibers are then spun into a web and bonded together by thermal or chemical treatment. This process creates a fabric with superior strength, breathability, and softness, making it an ideal choice for medical and hygiene products. Additionally, spun-bonded nonwovens offer better product consistency than other types of nonwoven fabrics and are more resistant to abrasion and water than other fabrics.
Wet-laid Nonwovens:
Wet-laid nonwovens are created by adding a binder to a web of fibers and then mixing and blending the fibers into a slurry. The mixture is then mixed, stirred, and spread onto a forming belt, allowing the fibers to form a web. The web is then dried, creating a strong, soft, and absorbent fabric. Wet-laid nonwovens are ideal for use in medical, hygiene, and feminine care products, as well as for automobile and industrial applications.
Melt-blown Nonwovens:
Melt-blown nonwovens are created using a process where synthetic polymer fibers are extruded through small holes and Onto a forming belt. The fibers are then melted and accreted onto the forming belt and laid in a “web” pattern. This process creates a lightweight, breathable fabric that is perfect for use in filtration and protective clothing.
SMS Nonwovens:
SMS nonwovens are created by bonding together layers of fiber with a sheet of plastic film. This process creates a strong and durable fabric that offers both breathability and waterproofing. SMS nonwovens are ideal for use in protective garments, medical and hygiene products, and even automotive parts. Needle-punched Nonwovens: Needle-punched nonwovens are created using a needle punching machine to punch closely spaced felting needles through multiple layers of fibers. The needles create loops in the fabric that are then interlocked with other fibers, forming a highly durable fabric. Needle-punched nonwovens are also known for their superior strength and durability, making them an ideal choice for garments, upholstery, and medical fabrics. Thermal-bonded Nonwovens: Thermal-bonded nonwovens are created using a heat-bonding technique. This process involves applying heat and pressure to a web of fibers, bonding them together and creating a fabric with superior strength and durability. Thermal-bonded nonwovens are ideal for use in medical and industrial applications, as well as infiltration and protective clothing.
In Conclusion:
These are just a few examples of nonwoven fabric examples that can be used in a variety of applications. Nonwoven fabrics offer a wide range of benefits, including superior strength, absorbency, and softness, making them ideal for use in medical, protection, and industrial applications. With their unique qualities, nonwoven fabrics have become an important tool for manufacturers, designers, and producers that wish to achieve a certain level of performance in their products. Nonwoven fabrics offer great value, making them an attractive option for a wide range of applications, from disposable items to luxury products.learn more(wikipedia)