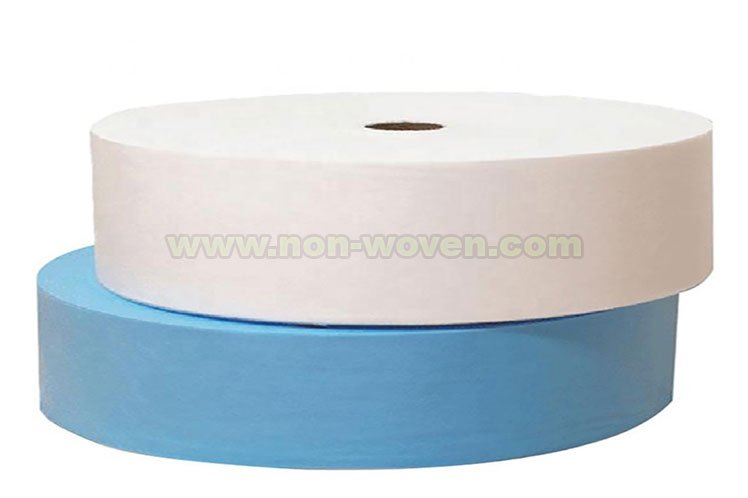
Classification of non woven fabric is a system used to categorize fabrics based on their physical and chemical properties. This system is important for the textile industry because it helps manufacturers choose the right fabric for their products. Non-woven fabrics are made from a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, metal, and glass.
The classification of non woven fabric is a complex process that is constantly evolving. The most common method of classification is by fiber type. This method is the most straightforward way to categorize fabrics. Other methods of classification include chemical composition, construction, and by weight.
manufacturers must keep up with the latest changes in the classification of non-woven fabrics to ensure that they are using the right fabric for their products.learn more(wikipedia)
Classification of Non Woven Fabrics:
Non-woven fabrics can be classified into three main categories based on how they are produced. Melt-based non-woven fabrics are created by melting synthetic fibers and processing them through a needle and spinnerette. Chemical bonding non-wovens are created by spraying or dipping synthetic fibers in a hot solution or binder and then allowing them to cool and bond. The stitching-based non-woven fabric uses a needle and thread to bond together pieces of synthetic fibers. Within each of these three main categories, non-woven fabrics can be further divided into various sub-categories. In melt-based non-wovens, for example, the fabrics can be divided into needle-punched, thermo-bonded and calendered types. Chemical bonding non-wovens can be further categorized as thermal, chemical and adhesive-bonded fabrics. No matter which type of non-woven fabric is chosen, it is important to understand its classification to ensure that the fabric will meet the desired requirements.
Characteristics of Non Woven Fabrics:
Non-woven fabrics are often described as being lightweight, flexible and breathable. They are strong enough to withstand the rigors of daily use and are relatively low cost. Additionally, non-woven fabrics can be produced in a wide range of colors, textures and thicknesses. These qualities make them ideal for a variety of applications. Non-woven fabrics are also permeable, meaning that air, water and other liquids can pass through them. This permeability allows the fabrics to act as filters, absorbing liquids and blocking particulates such as dust, bacteria and dirt. The fabrics can also absorb moisture, making them suitable for use in personal care products such as diapers and sanitary napkins. Non-woven fabrics are also flame retardant, meaning that they will not easily catch fire or produce toxic fumes. This makes them ideal for use in industrial and commercial applications.
Properties of Non Woven Fabrics:
Non-woven fabrics have several unique properties that make them ideal for a variety of applications. The fabrics are often described as ‘hygroscopic’ which means that they can absorb and retain moisture. This makes them well-suited for use in personal care products such as diapers and sanitary napkins. Non-woven fabrics also have a low linting property, meaning that they do not shed small fibers as traditional woven fabrics do. This makes them ideal for use in applications where linting is an issue, such as medical and food processing equipment. Non-woven fabrics are resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for use in products such as furniture, carpets and packaging. The fabrics also have good strength and durability, meaning that they can withstand a variety of conditions and are not easily damaged.
End-Uses of Non Woven Fabrics:
Non-woven fabrics have many applications in the textile industry. The fabrics are often used in apparel, such as in t-shirts, socks and underwear. The fabrics are also used in medical supplies, bedding and other products. Non-woven fabrics are also ideal for use in packaging, due to their strength and low linting properties. In addition to their traditional use in clothing and other household items, non-woven fabrics are increasingly being used in industrial applications. The fabrics are often used as filters, such as in air and water filtration systems. Additionally, they are ideal for use in composite materials, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Advantages of Non Woven Fabrics:
Non-woven fabrics offer many advantages over traditional woven fabrics. The fabrics are often much more lightweight, flexible and breathable, making them ideal for a variety of applications. Additionally, non-woven fabrics are hygroscopic, meaning that they can absorb and retain moisture. This makes them particularly suitable for use in items such as diapers and sanitary napkins. Non-woven fabrics also have a low linting property, meaning that they do not shed small fibers as traditional woven fabrics do. This makes them ideal for use in applications where linting is an issue, such as medical and food processing equipment. Finally, non-woven fabrics are resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for use in products such as furniture, carpets and packaging.
Disadvantages of Non Woven Fabrics:
Although there are many advantages to using non-woven fabrics, there are also some disadvantages. Non-woven fabrics are not as strong and durable as traditional woven fabrics, making them less suitable for use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, non-woven fabrics can be expensive, due to the complex and somewhat tedious process used to create them. Non-woven fabrics also tend to be more permeable than traditional woven fabrics, meaning that they do not provide as much insulation. This can be an issue in applications where temperature stability is important, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.