Introduction
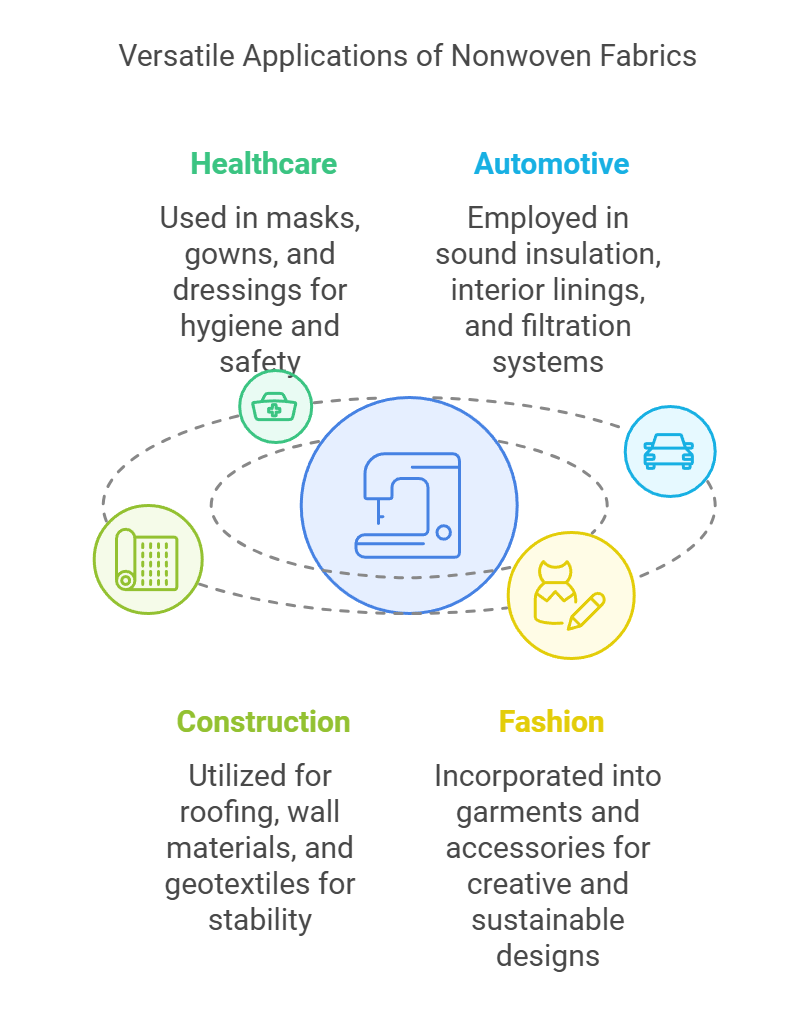
The diversification of uses for nonwoven fabric is particularly noteworthy, as this material has found applications in various sectors, including healthcare, automotive, construction, and fashion. In healthcare, nonwoven materials are widely employed in surgical masks, gowns, and wound dressings. Their lightweight and breathable nature makes them ideal for hygienic and disposable products that ensure safety and comfort for patients and healthcare professionals alike. In the automotive industry, nonwoven fabrics are utilized in sound insulation, interior linings, and filtration systems, contributing to enhanced performance and passenger comfort.
Moreover, nonwoven fabrics play a vital role in the construction field, often used for roofing and wall materials due to their moisture-resistant properties. These fabrics can also act as geotextiles, providing stabilization and erosion control in civil engineering projects. The fashion industry is not left behind; innovative designers are increasingly incorporating nonwoven textiles into garments, accessories, and sustainable fashion collections. The adaptability of nonwoven fabrics allows for creative expression while addressing sustainability challenges.
As industries continue to evolve, the diverse applications of nonwoven fabric will likely expand further, reflecting the ongoing innovation in material science. This blog post aims to explore the various uses of nonwoven fabric, illuminating its role and importance across these dynamic sectors.
Understanding Nonwoven Fabrics
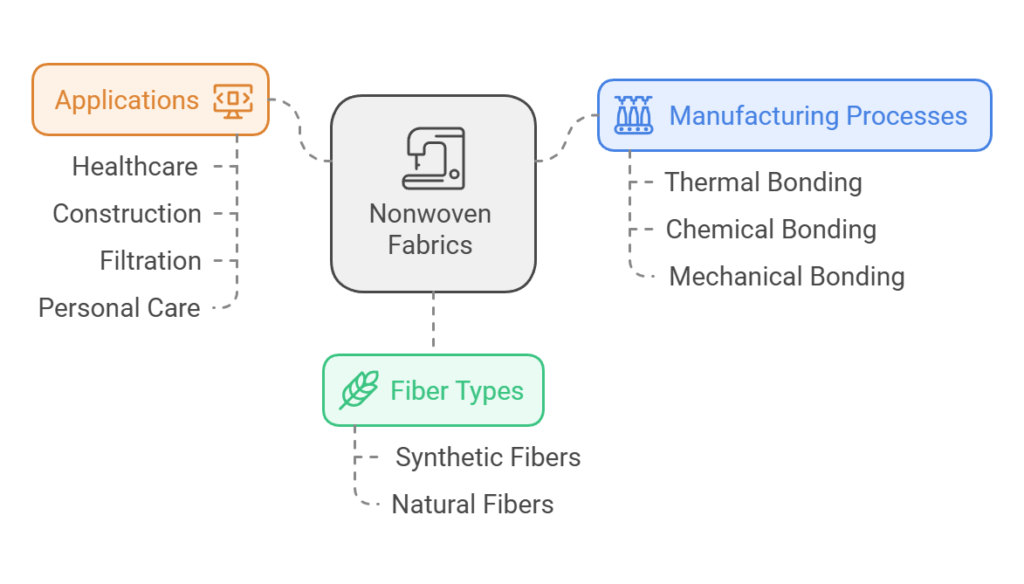
Nonwoven fabrics are a unique category of textile material that differ significantly from traditional woven or knitted fabrics. Unlike these conventional textiles, nonwoven fabrics do not consist of interlacing yarns. Instead, they are manufactured by directly bonding together fibers using various methods, resulting in a versatile and distinct fabric type that offers a plethora of applications.
The manufacturing process of nonwoven fabrics involves several techniques, including thermal bonding, chemical bonding, and mechanical bonding. In thermal bonding, heat is used to partially melt and fuse the fibers, creating a sturdy fabric. Chemical bonding employs adhesives or chemicals to bind fibers together, typically resulting in a fabric characterized by high strength and durability. Mechanical bonding, on the other hand, physically entangles the fibers through processes like needle punching or hydro-entangling, producing a structure that resembles traditional materials yet retains unique properties.
In terms of fiber types, nonwoven fabrics can be made from a range of materials, including synthetic fibers such as polyester and polypropylene, as well as natural fibers like cotton. The choice of fiber influences the fabric’s characteristics, such as moisture absorption, softness, and strength. Additionally, the versatility of nonwoven fabric structures allows for various applications across industries, including healthcare, construction, filtration, and personal care products.
One key characteristic that sets nonwoven fabrics apart from their woven counterparts is their ability to be produced in large quantities with tailored properties to meet specific needs. As such, they are often utilized in disposable products due to their cost-effectiveness and performance features. Understanding nonwoven fabrics, their manufacturing processes, and unique characteristics is essential for exploring their diverse applications across different sectors.
Applications of Nonwoven Fabrics in Healthcare
Nonwoven fabrics play a pivotal role in the healthcare sector, offering innovative solutions that cater to various medical applications. These fabrics are predominantly used in medical textiles, which include a range of products designed to enhance patient care and ensure optimal hygiene standards. The unique properties of nonwoven materials—such as their breathable nature, lightweight composition, and cost-effectiveness—make them particularly suitable for both disposable and reusable medical items.
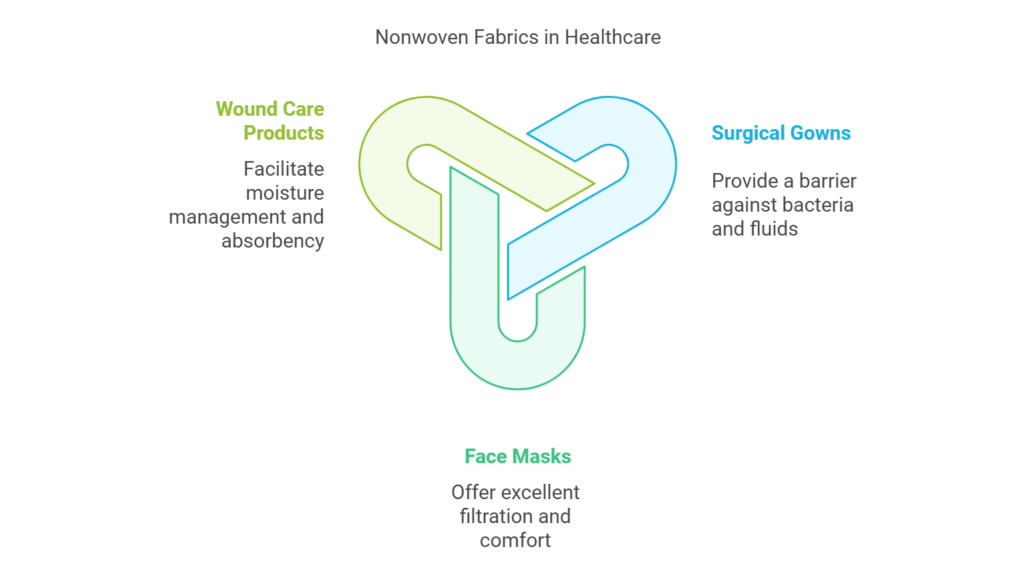
One of the most significant applications of nonwoven fabrics is in the production of surgical gowns. These gowns must meet stringent safety and hygiene standards to protect healthcare professionals and patients. Nonwoven materials, by virtue of their structure, provide a barrier against bacteria and bodily fluids, thus minimizing the risk of infections during surgical procedures. Additionally, they are designed for easy donning and removal, further enhancing the efficiency of surgical teams.
Face masks, especially in light of recent global health challenges, have seen a remarkable advancement in their design and materials. Nonwoven fabrics have become the preferred choice for these protective masks due to their excellent filtration capabilities. They can effectively block pathogens and particulate matter while remaining comfortable for prolonged use. The three-ply structure commonly found in surgical masks is often composed of nonwoven materials, ensuring an adequate balance between protection and breathability.
Wound care products also extensively utilize nonwoven fabrics, as they facilitate moisture management and provide cushioning for injuries. Nonwoven dressings are favored for their superior absorbency, allowing for enhanced healing while keeping the wound area clean and dry. Overall, nonwoven materials in healthcare not only support patient safety and comfort but also enhance clinical outcomes through their innovative applications.
Nonwoven Fabrics in the Automotive Industry
Nonwoven fabrics have become an integral component in the automotive industry, serving a myriad of applications that enhance vehicle performance and contribute to overall sustainability. One of the primary uses of these fabrics is in sound insulation. Automotive manufacturers utilize nonwoven materials to minimize noise levels within the cabin, providing a quieter and more comfortable driving experience. The properties of nonwoven fabrics allow them to absorb sound effectively, which is essential in modern vehicles that require a higher level of acoustic comfort.
In addition to sound insulation, nonwoven fabrics play a vital role in filtration systems within vehicles. They are known for their exceptional filtration capabilities, which help in ensuring that air and fluid systems remain clean and efficient. Nonwoven filters can effectively trap dirt, dust, and other particulates, thus enhancing the longevity and performance of vital vehicle components such as the engine and air conditioning system. This not only improves vehicle reliability but also contributes to lower emissions, aligning with the automotive industry’s shift towards greener technologies.
Upholstery is another significant application of nonwoven materials in the automotive sector. These fabrics provide superior durability and comfort, making them ideal for seat covers and interior linings. Their lightweight nature enables manufacturers to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which supports fuel efficiency and performance. Furthermore, the versatility of nonwoven fabrics allows for a variety of designs, colors, and textures, catering to consumer preferences and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of vehicles.
Another notable application is in the creation of lightweight structural components. Nonwoven fabrics can be engineered to provide strength while minimizing weight, which is crucial in the ongoing effort to improve energy efficiency in automotive design. As the industry continues to evolve, the versatility and performance characteristics of nonwoven fabrics make them a vital asset for future innovations in vehicle development.

The Role of Nonwoven Fabrics in Construction
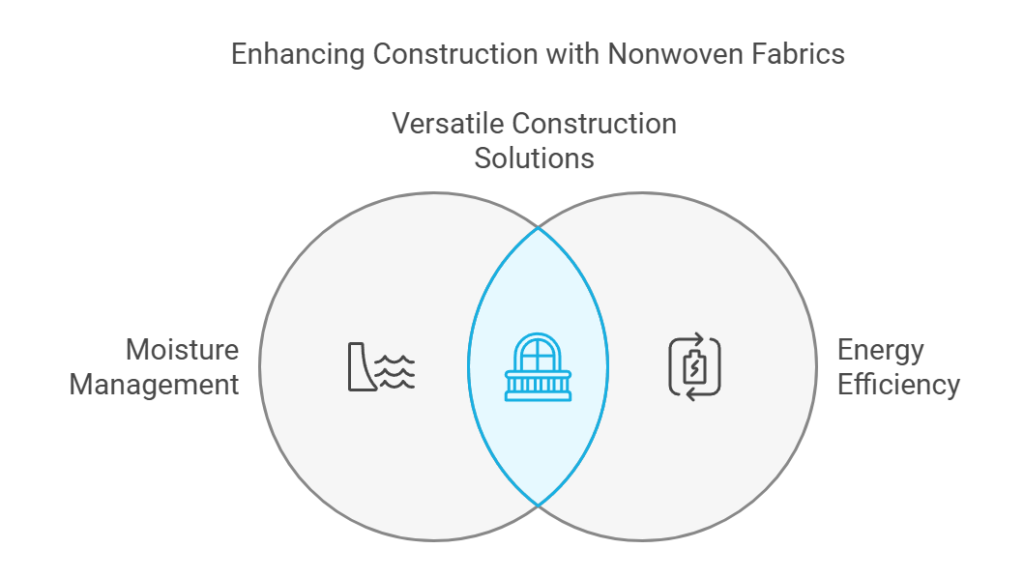
Nonwoven fabrics have established a significant presence in the construction industry, offering a diverse array of applications that enhance various building processes. These innovative materials are primarily utilized in geotextiles, insulation, and roofing membranes, due to their unique properties and benefits. One of the foremost advantages of using nonwoven fabrics in construction is their superior moisture management capabilities. This attribute is crucial, especially in geotextile applications, where the fabrics serve to control water flow, prevent soil erosion, and enhance drainage systems.
In terms of insulation, nonwoven fabrics contribute to energy efficiency within buildings. With the growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices, these materials are being increasingly adopted for thermal insulation purposes. They are lightweight yet provide considerable thermal resistance, which aids in minimizing heat loss during colder months and keeping interiors cooler during the summer. Moreover, their excellent air permeability allows for adequate ventilation, reducing the risk of condensation and mold growth, which can compromise the structural integrity of buildings.
Roofing materials made from nonwoven fabrics are also gaining traction, particularly in the production of underlayments that provide an additional layer of protection against moisture infiltration. These nonwoven solutions are designed to withstand the harsh conditions often encountered in construction sites, such as high winds and heavy rainfall. Their durability is a noteworthy characteristic, as nonwoven fabrics demonstrate resilience and longevity, lowering maintenance costs over time.
Overall, nonwoven fabrics represent an essential material in modern construction, owing to their versatility and beneficial properties. As the industry continues to innovate, these fabrics will play an increasingly crucial role in achieving enhanced performance and sustainability in building projects.
Innovative Uses in Fashion and Textiles
The fashion industry is increasingly recognizing the potential of nonwoven fabrics, especially as sustainability becomes a pressing concern among consumers and designers alike. Nonwoven fabrics, crafted from fibers that are bonded together through various processes rather than woven, present versatile opportunities for innovative design and environmentally friendly production in fashion.
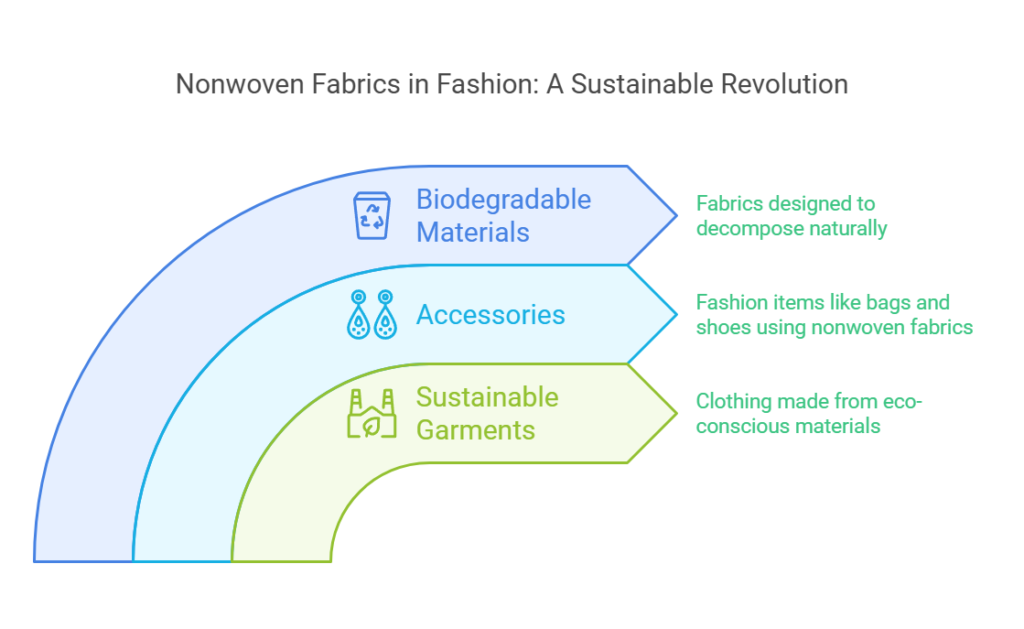
One noteworthy application of nonwoven materials in fashion is the creation of sustainable garments. These fabrics can be engineered to provide breathability and durability, characteristics essential for modern apparel. Emerging trends feature the use of nonwoven fabrics to produce stylish yet functional clothing items that cater to the desires of eco-conscious consumers. Designers are increasingly utilizing these nontraditional materials to create dramatic silhouettes and intricate textures, which enhance aesthetic appeal while reducing environmental impact.
In addition to clothing, nonwoven fabrics are making their mark in the accessory market. Bags, hats, and shoes made from nonwoven materials have gained popularity due to their lightweight nature and versatility in design. Noteworthy brands are adopting these fabrics to create innovative collections that emphasize sustainable practices without compromising on style. The properties of nonwoven textiles, such as water resistance and ease of maintenance, further strengthen their position in accessory fashion.
With environmental awareness growing, the development of biodegradable nonwoven materials is an emerging trend worth mentioning. These innovative textiles not only provide design flexibility but also fulfill the market’s demand for products capable of decomposing naturally at the end of their life cycle. As designers continue to experiment with this eco-friendly approach, nonwoven fabrics stand out as a promising solution to blend fashion with sustainability, fostering an industry shift toward responsible consumption.
Sustainability and the Future of Nonwoven Fabrics
The conversation surrounding sustainability has gained considerable momentum in recent years, particularly in textile manufacturing, where the advent of nonwoven fabrics has opened a range of possibilities. Nonwoven fabrics, known for their versatility and innovative applications, also face scrutiny regarding their environmental impact. Hence, addressing sustainability concerns is pivotal to the future direction of this industry. One of the key challenges is the recycling of nonwoven materials. As they are often created from synthetic fibers, their biodegradability can be limited, posing significant challenges at the end of their lifecycle. Traditional recycling methods have not been widely applied to nonwoven fabrics, primarily due to their multi-layered structure and varied fiber compositions. However, there are increasing efforts to develop innovative recycling technologies, aimed at enhancing the circular economy within the textile sector.
Opportunities also arise in the form of biodegradable nonwoven materials, which have started to gain traction. These alternatives, often derived from renewable resources such as cellulose or biopolymers, promise a more environmentally friendly solution. They can break down naturally, thus addressing the pressing issue of plastic pollution associated with synthetic options. The growing consumer demand for sustainable products has spurred the research and development of these green materials, creating a promising avenue for future innovation.
Additionally, trends indicate that manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices throughout the production process. This includes minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and utilizing eco-friendly dyes and finishes. As businesses align with global sustainability goals, the nonwoven fabric sector is likely to evolve, presenting new opportunities for brands to meet consumer expectations while remaining environmentally responsible. The integration of sustainable practices alongside advancements in material technology signals a vital shift towards a more sustainable future for nonwoven fabrics.

Frequently Asked Questions
Nonwoven fabrics have gained prominence in various industries due to their unique properties. One of the primary benefits of nonwoven fabrics is their versatility. They can be engineered to meet specific requirements for different applications, including hygiene products, medical supplies, and geotextiles. Their ability to combine properties such as softness, strength, and absorbency makes them an attractive option for manufacturers. Additionally, nonwoven fabrics are typically lighter than traditional fabrics, which can reduce shipping costs and material usage.
Another common query pertains to the recyclability of nonwoven fabrics. The recyclability largely depends on the materials used in the production of the nonwoven fabric. For instance, those made from polypropylene can be recycled, while others may not be as readily recyclable. However, the textiles industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability, resulting in a rising number of nonwoven products being made from recycled materials or designed to be more environmentally friendly. Many manufacturers are also investigating methods to improve the recycling process for nonwoven fabrics, ensuring they contribute less waste to landfills.
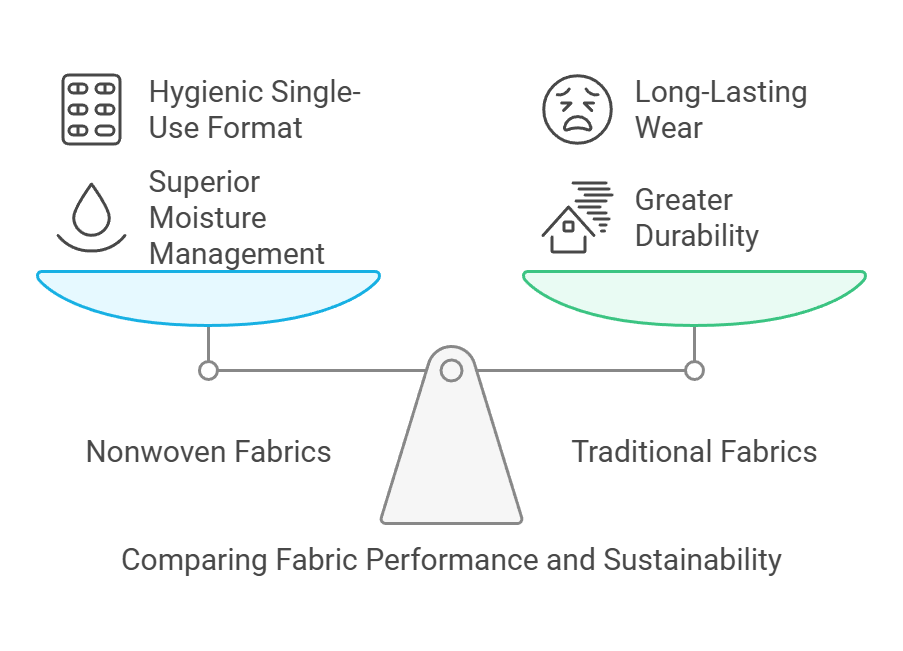
When comparing nonwoven fabrics to traditional fabrics in terms of performance, several factors come into play. Nonwoven fabrics offer superior performance in certain applications, especially where moisture management and filtration are required. For example, in medical contexts, nonwoven materials are favored for their hygienic properties and ability to be manufactured in single-use formats. Traditional fabrics, while often more durable in terms of wear and tear, may not provide the same level of performance in terms of filtration or absorbency. Therefore, the choice between nonwoven and traditional fabrics depends largely on the specific requirements of the intended use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nonwoven fabrics have demonstrated remarkable versatility across various industries, showcasing their ability to adapt to diverse applications. Prolific uses range from healthcare products such as surgical gowns and masks to everyday household items like cleaning wipes and diapers. The unique properties of nonwoven materials, including their lightweight nature, breathability, and durability, make them increasingly popular in sectors such as automotive, construction, and agriculture.
The ongoing innovation in nonwoven fabric production techniques has paved the way for the development of specialized materials tailored to specific needs. For instance, advancements in manufacturing processes, such as spunbond and meltblown technologies, have enhanced the performance characteristics of nonwoven fabrics. These advances enable the creation of tailored solutions that serve the unique requirements of varying applications, further diversifying their uses.
As industries seek sustainable alternatives, the role of nonwoven fabrics is expected to grow. Organizations are actively investigating eco-friendly materials and production practices that align with environmental objectives. The emphasis on sustainability can lead to the introduction of biodegradable nonwoven fabrics, thus contributing to a circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin resources.
Overall, the expanding applications of nonwoven fabrics reflect the dynamic nature of this sector. Industry stakeholders must prioritize collaboration, research, and development to fully unleash the potential of nonwoven fabrics in addressing contemporary challenges. Continuous investment in innovative solutions will not only support the growth of this market but also ensure its contributions to sustainability and resource efficiency are maximized, paving the way for broadened uses and enhanced performance across various industries.

14 Responses
“Great content, learned a lot from this post!”
Thank you! Glad you found it useful.
“This is exactly what I was looking for, thank you!”
Glad it was helpful!
Glue Dream strain This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.
Thank you! Glad you liked it.
I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble You are amazing Thanks
Thank you! I’m glad to hear that the website has been helpful to you.
Thanks I have recently been looking for info about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far However what in regards to the bottom line Are you certain in regards to the supply
Thanks! I have recently been looking for info about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
If you have any further questions or need to discuss this topic in more detail, feel free to reach out to me via WhatsApp at +86 13599755808. I’m always happy to engage in conversations related to this field.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you’ve enjoyed our blog posts. Your support means a lot to us, and we’ll keep sharing more great content. Stay tuned!
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here The sketch is attractive your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re glad you like our article. We’ll keep up the good work and look forward to your continued visits.