Introduction to Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics are engineered textile materials made from fibers that are bonded together mechanically, thermally, or chemically, as opposed to conventional woven or knitted fabrics which utilize a structure of interlaced threads. This unique manufacturing process allows for a diverse range of textile applications across various industries. Nonwoven fabrics exhibit distinct characteristics, including lightweight properties, durability, and versatility, which have contributed to their growing significance in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, construction, and consumer products.
The versatility of nonwoven fabrics is notable, as they can be engineered to meet specific requirements such as absorptive qualities, waterproofing, and filtration capabilities. This adaptability makes them suitable for a plethora of applications. For instance, in the medical field, nonwoven materials are extensively used in surgical masks, gowns, and wound dressings, providing essential barriers against contamination. In the automotive industry, nonwovens serve as insulation, soundproofing, and a variety of interior components. Their lightweight and cost-effective nature also makes them a popular choice in the manufacture of disposable products, such as diapers and hygiene products.
Furthermore, the sustainability of nonwoven fabrics is becoming increasingly important, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly fibers and production methods. The potential for recycling and reusing nonwoven materials contributes to a more sustainable approach within the textile industry. As consumer awareness of environmental issues rises, nonwoven fabrics offer innovative solutions that align with sustainable practices.
In summary, nonwoven fabrics are integral to countless applications due to their unique properties, versatility, and the ongoing advancements in manufacturing processes. Understanding these essential fabrics provides a foundational context for delving into the complexities of their manufacturing processes.
What is the Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing Process?
The nonwoven fabric manufacturing process is a sophisticated approach that involves converting raw polymer into sheets of fabric without the traditional weaving or knitting processes. The production of nonwoven fabrics typically comprises several essential steps, including polymer formation, web formation, bonding, and finishing.
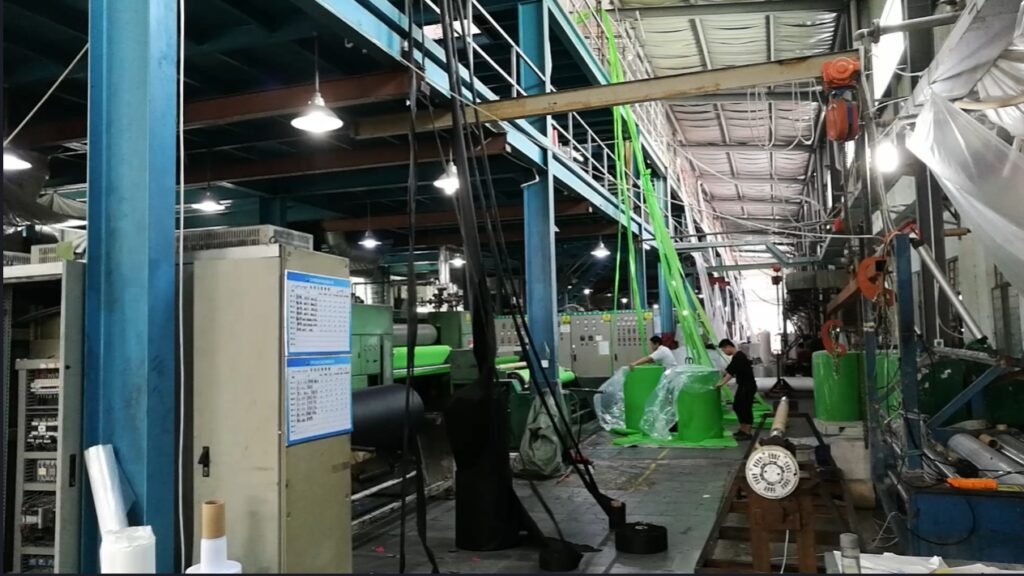
The initial phase begins with the selection of raw materials, which usually involve synthetic fibers such as polypropylene or polyester. These fibers are then softened through a melting process. Once the polymer is liquefied, it can be processed using various methods. One of the most commonly used techniques is spunbonding. In this method, the melted polymers are extruded through spinnerets, generating continuous filaments that are cooled and laid down onto a conveyor belt to form a web.
Another prevalent technique is dry laying. In this process, staple fibers are mechanically opened, carded, and laid down to create a web structure. The resultant web can then undergo additional processes to enhance its properties. Similarly, the wet laying method involves dispersing fibers in water to form a slurry, which is then deposited onto a screen where the water is drained, leaving behind a mat of fibers.
Once a web is formed, the next critical step is bonding. This can be achieved through several methods, including thermal bonding, where heat is applied to fuse the fibers, or chemical bonding, using adhesives to bond the material together. Finally, the nonwoven fabric may undergo various finishing processes, such as coating or dyeing, to enhance its appearance and performance characteristics. This comprehensive framework of techniques illustrates the complexity and versatility of the nonwoven fabric manufacturing process, catering to a wide array of applications from medical supplies to household products.
Types of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics are categorized based on their manufacturing processes and applications, resulting in a diverse range of types each suited for specific uses. Understanding these categories can greatly enhance comprehension of the nonwoven fabric industry’s capabilities.
One prominent category is spunbond nonwoven fabrics. This type is produced by continuously melting thermoplastic materials, extruding them into filaments, and randomly laying them on a conveyor. The filaments are subsequently bonded through thermal or chemical means. The resulting spunbond fabrics are known for their strength, durability, and flexibility, making them ideal for applications such as geotextiles, agricultural covers, and hygiene products.
Another significant category is meltblown nonwoven fabrics, which utilizes a similar melting process but employs a different technique to create finer fibers. Meltblown fabrics are formed by forcing the molten polymer through a die, which produces a web of extremely fine fibers. These fine particles create a fabric with excellent filtration efficiency, commonly used in filtration products, face masks, and absorbent materials.
Needle-punched nonwoven fabrics are created through a mechanical process that entangles fibers together using barbed needles. This method enhances the fabric’s structure and strength, leading to applications in various industries including automotive, construction, and home textiles. Needle-punched fabrics are recognized for their breathability and insulation properties, providing additional versatility in usage.
These categories reflect just a few examples of the extensive array of nonwoven fabrics available. Each type is manufactured based on unique processes and specific performance criteria, catering to a wide variety of uses in both consumer goods and industrial applications. Understanding these fabric types can assist designers and manufacturers in making informed decisions about materials best suited for their requirements.
Materials Used in Nonwoven Fabric Production
Nonwoven fabric production involves an array of raw materials, each contributing to the distinct properties and applications of the final product. Among the most prominent materials is polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its lightweight and durable characteristics. Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are widely used in several industries, including hygiene products, medical applications, and construction, due to their excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals.
Another significant material in the nonwoven fabric sector is polyester. Known for its strength and resilience, polyester offers superior performance in terms of dimensional stability and resistance to stretching or shrinking. This makes polyester-based nonwoven fabrics particularly suitable for items such as geotextiles, automotive components, and filter media. The choice of polyester also enhances the fabric’s aesthetic features and can be tailored to meet specific environmental requirements.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in biodegradable options, as the demand for eco-friendly materials continues to rise. Biodegradable nonwoven fabrics can be manufactured from natural fibers such as cotton, jute, or bamboo, as well as from synthetic fibers that are derived from renewable resources. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also cater to consumer preferences for sustainable options. The production of such fabrics questions the balance between traditional material durability and environmental considerations.
Ultimately, the selection of raw materials significantly influences the characteristics of nonwoven fabrics. Factors such as the intended application, desired properties, and manufacturing configurations drive this decision-making process. A thorough understanding of the various materials available, including polypropylene, polyester, and biodegradable alternatives, is crucial for manufacturers seeking to produce high-quality nonwoven fabrics tailored to specific markets.
The Manufacturing Process Explained
The production of nonwoven fabrics is a sophisticated process that involves several meticulously coordinated stages. The journey begins with fiber preparation, where raw materials such as polypropylene, polyester, or other fibers are selected based on the desired characteristics of the final product. These fibers may be in the form of staple fibers or continuous filaments, which are subsequently carded or opened to align the fibers for the next step.
Once the fibers are prepared, they undergo the process of formation. During this phase, various techniques can be employed to create a web of fibers. Common methods include spunbonding, where molten polymers are extruded through spinnerets and cooled to form a web, and carding, which involves mechanically entwining fibers to produce a continuous mat. The chosen method significantly impacts the properties of the nonwoven fabric, such as strength, texture, and appearance.
After the fibers are formed into a web, the bonding process occurs. This can be achieved through mechanical, thermal, or chemical means. Mechanical bonding involves entangling the fibers, often using needle punching. Thermal bonding uses heat to melt and fuse fibers together, while chemical bonding involves applying adhesive agents. Each bonding technique alters the fabric’s properties and dictates its suitability for various applications.
The final stage of nonwoven fabric production is finishing. This includes processes that enhance the fabric’s performance and aesthetic qualities. Common finishing treatments may involve calendaring, dyeing, or the application of finishes that impart water resistance or antimicrobial qualities. The overall quality of the nonwoven fabric is further evaluated through rigorous testing to ensure it meets industry standards.
With a clear understanding of each stage in the nonwoven fabric manufacturing process, one can appreciate the complexity and craftsmanship involved in creating these versatile materials.
Applications of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have emerged as versatile materials with a broad spectrum of applications across various industries. Their unique properties, such as lightweight, strength, and absorbency, along with cost-effectiveness, make them essential in numerous sectors. One of the most prominent applications is in the healthcare industry, where nonwoven materials are utilized for items like surgical masks, gowns, and drapes. The bacterial barrier properties of these fabrics contribute significantly to infection control, making them indispensable in medical settings.
In addition to healthcare, nonwoven fabrics play a crucial role in hygiene products. They are commonly employed in the production of disposable diapers, feminine hygiene products, and adult incontinence pads. These fabrics provide superior fluid management and comfort, contributing to the overall effectiveness of hygiene solutions. The ability to tailor nonwoven materials to specific absorbency levels and softness is an advantage that further solidifies their use in this field.
The automotive industry also takes advantage of nonwoven fabrics, utilizing them for sound insulation, filtration, and interior materials. Their lightweight nature contributes to fuel efficiency while maintaining structural integrity, making them an ideal choice for various automotive components. Moreover, nonwoven fabrics are used in the production of carpets and upholstery, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality within vehicles.
Beyond these sectors, nonwoven fabrics are increasingly found in consumable products such as wipes and cleaning cloths. Their ability to trap dirt and moisture effectively has made them a staple in households and commercial cleaning applications. With innovations continuing to expand the possibilities for nonwoven materials, their significance across industries is expected to grow, showcasing their adaptability and efficiency in addressing various needs.
Advantages of Nonwoven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics have become increasingly popular across various industries, and this rise in demand can be attributed to numerous advantageous properties that these materials offer. One of the primary benefits of nonwoven fabrics is their cost-effectiveness. The manufacturing process involves bonding fibers together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical means, which often requires less material and energy compared to traditional woven fabrics. As a result, manufacturers can produce nonwovens with lower production costs, leading to more affordable end products.
In addition to economic benefits, nonwoven fabrics are characterized by their lightweight properties. This feature makes them an ideal choice for a variety of applications, including disposable products such as surgical gowns, face masks, and hygiene products. The lightweight nature of nonwovens not only facilitates ease of transport and handling but also enhances comfort for the end-users. This attribute has made nonwoven fabrics a preferred choice in sectors where weight is a significant consideration.
Furthermore, the versatility of nonwoven fabrics adds to their appeal. They can be manufactured to combine various qualities such as breathability, water resistance, and durability, making them suitable for diverse applications ranging from geotextiles in construction to insulating materials in the automotive industry. The ongoing innovation in nonwoven technologies allows manufacturers to tailor the properties of these fabrics to meet specific needs, ultimately expanding their utility across different sectors. This adaptability is a critical driver behind the growing popularity of nonwoven fabrics in today’s market. Overall, the combination of cost-effectiveness, lightweight characteristics, and versatility positions nonwoven fabrics as a robust alternative to traditional textile materials.
Challenges in the Nonwoven Fabric Industry
The nonwoven fabric industry faces a variety of challenges that impact its growth and efficacy. One significant concern revolves around environmental sustainability. The production processes of nonwoven fabrics often involve the use of synthetic materials that can contribute to pollution and increased landfill waste. As consumers obtain a heightened awareness regarding environmental issues, there is increased pressure on manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as utilizing biodegradable materials or recycling processes. Addressing these environmental concerns is not just essential for marketability, but also crucial for compliance with evolving regulations.
Competition from traditional fabrics presents another challenge for the nonwoven sector. Established materials like cotton, wool, and polyester have well-known attributes that consumers often prefer, making it difficult for nonwoven fabrics to gain market share. This competitive landscape necessitates that nonwoven fabric manufacturers continuously innovate and highlight their unique selling propositions, which may include advantages such as lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and diverse applications. If nonwoven materials cannot convincingly demonstrate their benefits over traditional fabrics, they risk stagnation in a crowded marketplace.
Moreover, the need for technological advancements remains a persistent issue within the industry. Although there have been impressive developments in nonwoven technology, including new manufacturing techniques and enhanced material properties, the sector must continually adapt to maintain relevance. This may involve significant investments in research and development to optimize production processes and create innovative products that meet changing consumer demands. The pace of innovation in this area is critical, as competitors from both the synthetic and natural fiber markets continue to emerge, pushing the boundaries of quality and performance.
FAQs About Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing
Nonwoven fabrics have gained considerable attention in recent years due to their versatile applications and unique manufacturing processes. A common question arises: what differentiates nonwoven fabrics from woven or knitted alternatives? The primary distinction lies in their production method. Unlike traditional textiles, which interlace yarns in a loom or use knitting techniques, nonwoven fabrics are created by bonding fibers together through various mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes. This results in a fabric that can have distinct properties tailored for specific uses, ranging from filtration to medical applications.
Another prevalent inquiry pertains to the sustainability of nonwoven materials. Many assume that the absence of traditional weaving techniques translates to a lack of eco-friendliness. However, many nonwovens are made from recyclable materials and are designed for biodegradability. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing processes have led to the creation of more energy-efficient production methods, further enhancing the sustainability of nonwoven fabrics. As a result, nonwoven textiles can serve as an environmentally conscious alternative compared to their woven counterparts when sourced responsibly.
It’s also essential to address some common myths surrounding nonwoven fabrics. One prevalent misconception is that they are inferior in quality compared to traditional textiles. In reality, nonwoven fabrics are engineered for specific durability and performance features. They can be designed to offer strength and resilience, making them suitable for diverse applications such as medical gowns, insulation, and geotextiles. Furthermore, nonwoven fabrics can be produced in varied styles and thicknesses, catering to both functional and aesthetic needs.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of nonwoven fabrics helps dispel myths and highlights their unique properties. By exploring these frequently asked questions, consumers can make informed choices regarding their use and benefits in various industries.

12 Responses
Hello my loved one I want to say that this post is amazing great written and include almost all significant infos I would like to look extra posts like this
Thanks for your compliment! Glad you liked the post. 😊
Family Dollar Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
hanks! Glad you liked it.
My brother recommended I might like this web site He was totally right This post actually made my day You cannt imagine just how much time I had spent for this information Thanks
Glad you liked the site and the post! 😊
Newtoki Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
Thanks for your kind words! Glad you liked it. Will keep sharing. 😊
Somebody essentially help to make significantly articles Id state This is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual post incredible Fantastic job
Thank you for your kind words! We will continue to provide valuable content.
Noodlemagazine This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
Welcome! Glad you find everything useful. 😊